If you have ever stood in front of a hardware shelf, scrolled through an online supplier’s catalog, or worked on a project where tubing was involved, you already know one thing: tube sizes can be confusing. Numbers don’t always mean what we think they mean, charts look technical, and one small mistake can turn into wasted money, time, and effort.
That’s exactly why this Tube Size Chart 2026 explained guide exists.
This article is written to feel like a real conversation — not a textbook. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, a mechanic, a fabricator, or someone just trying to order the correct tube for the first time, this guide will help you understand tube sizes clearly, calmly, and practically.
Why Tube Size Matters More Than You Think
Tube size plays a critical role in how a system performs, lasts, and stays safe. Many people focus only on fit, but proper sizing directly impacts strength, efficiency, and reliability in both professional and DIY projects.
Tube size is not just about “will it fit?” It affects:
Strength and load capacity
Fluid or air flow
Welding and fabrication accuracy
Compatibility with fittings
Safety and durability
Choosing the wrong tube diameter or thickness can lead to leaks, weak joints, vibration issues, or complete system failure. In industrial work, that can be expensive. In home projects, it can be frustrating and time-consuming.
In 2026, with more precision tools, CNC fabrication, and modular designs becoming common, accurate tube sizing is more important than ever.
Tube vs Pipe: A Quick but Important Difference
Before looking at size charts, it’s important to clear up a common confusion. Tubes and pipes may look similar, but they are measured and used differently. Understanding this difference helps you choose the right material and avoid costly sizing mistakes.
Tubes are measured by outside diameter (OD) and wall thickness
Pipes are measured by nominal size and schedule
This article focuses only on tubes, not pipes. If you apply pipe sizing logic to tube measurements, the numbers will quickly become confusing and inaccurate.
Understanding Tube Size Terminology (In Simple Words)
Tube size charts may look technical, but they rely on a few basic terms. Once you understand these, reading any tube chart becomes much easier. These measurements explain how wide a tube is, how thick its walls are, and how much space is available inside.
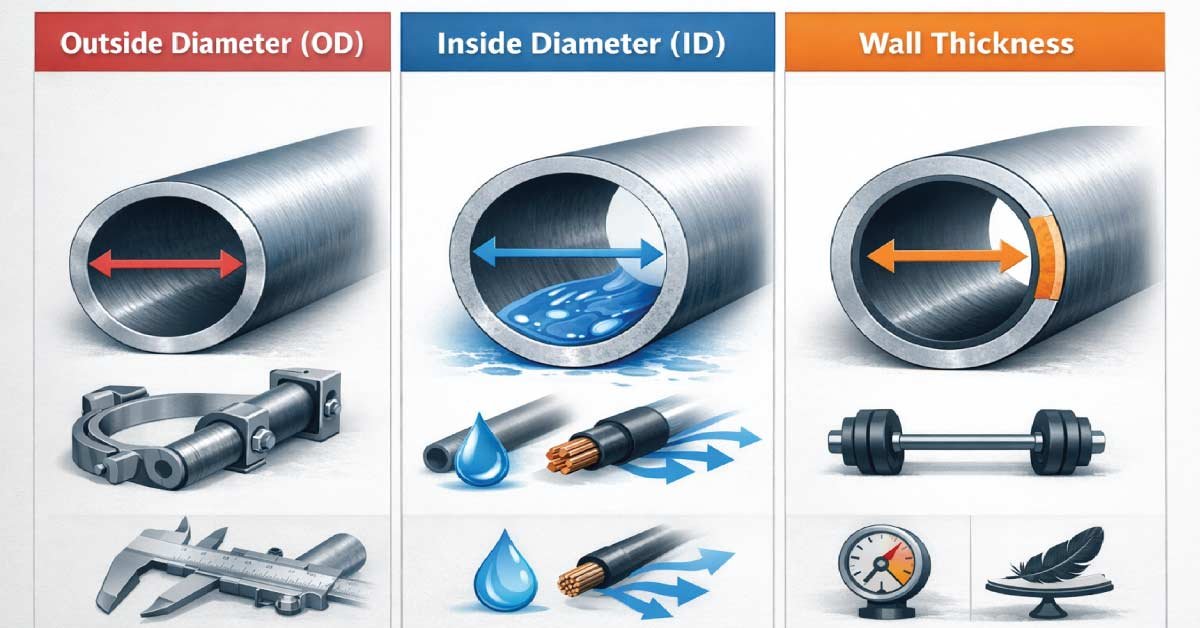
1- Outside Diameter (OD)
OD is critical because:
- It determines whether the tube fits into clamps or brackets
- It affects bending and alignment
- Most tube charts are based on OD
2- Inside Diameter (ID)
The inside diameter (ID) is the clear space within a tube. It determines how much fluid, air, or wiring can pass through and affects flow, clearance, and overall functionality. Choosing the right ID ensures your tube fits its intended purpose while avoiding blockages, leaks, or inefficient performance.
This matters most when:
- Fluids, air, or wires pass through the tube
- Flow rate is important
- Clearance is required
ID is calculated using:
ID = OD – (2 × wall thickness)
3- Wall Thickness
Wall thickness measures how strong and rigid a tube is. It affects the tube’s weight, pressure tolerance, and durability. Thicker walls provide strength and stability, while thinner walls reduce weight and cost. Understanding wall thickness helps you select the right tube for structural integrity, bending needs, and safe operation.
Thicker walls mean:
- More strength
- Higher pressure tolerance
- More weight
Thinner walls mean:
- Lighter weight
- Easier bending
- Lower cost (in many cases)
Also Read:
Struggling to pick the right lag bolt sizes for heavy-duty projects? 👉 This guide explains everything about diameter, length, and load capacity to ensure strong, secure fixing. Avoid weak joints and costly mistakes—read the full post now and choose the perfect lag bolts for any construction or DIY project with confidence!
How Tube Size Charts Are Structured in 2026
Modern tube size charts in 2026 are easier to read and more user-friendly, but their basic structure remains familiar. They typically show outside diameter (OD), wall thickness options, inside diameter (ID), weight per length, and material type. Advanced charts may include pressure ratings, tolerance limits, and metric/imperial conversions. Dual-unit charts (mm and inches) are now common, simplifying global sourcing and selection for all projects.
Common Tube Sizes You will See Most Often
While there are hundreds of tube sizes, some are used far more frequently in everyday projects. Knowing these common sizes helps you choose the right tube for applications like automotive frames, furniture fabrication, handrails, machinery structures, and fitness equipment.
| Measurement System | Common Outside Diameters (OD) |
|---|---|
| Imperial | 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch, 1 inch, 1.5 inch, 2 inch |
| Metric | 10 mm, 12 mm, 20 mm, 25 mm, 50 mm |
These sizes are widely applied in construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects, making them essential for both beginners and professionals.
Complete Tube Size Chart 2026
Tube sizes vary widely, but certain diameters and wall thicknesses are used most often in everyday projects. Understanding both imperial and metric sizes helps you choose the right tube for strength, flow, and fit. This 2026 guide covers common OD and ID measurements, wall thickness, and typical applications for accurate, reliable selection.
| Measurement System | Outside Diameter (OD) | Wall Thickness (Common) | Inside Diameter (ID) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imperial | 1/2 inch | 0.065–0.120 inch | 0.26–0.37 inch | Furniture frames, handrails, DIY projects |
| 3/4 inch | 0.065–0.154 inch | 0.44–0.62 inch | Automotive frames, light machinery | |
| 1 inch | 0.065–0.188 inch | 0.62–0.87 inch | Fitness equipment, structural supports | |
| 1.5 inch | 0.083–0.203 inch | 1.09–1.33 inch | Medium machinery, handrails | |
| 2 inch | 0.095–0.218 inch | 1.56–1.81 inch | Industrial frames, automotive chassis | |
| Metric | 10 mm | 1–2 mm | 8–8.5 mm | Furniture, light tubing |
| 12 mm | 1–2 mm | 10–10.5 mm | Handrails, small frames | |
| 20 mm | 1–3 mm | 17–18 mm | Automotive, machinery | |
| 25 mm | 1–3 mm | 22–23 mm | Industrial equipment, fitness | |
| 50 mm | 2–4 mm | 42–46 mm | Structural supports, pipelines |
Notes:
OD is the outside diameter, ID is inside diameter (ID = OD – 2 × wall thickness).
Wall thickness varies depending on material (steel, aluminum, stainless) and application.
This chart is meant for general reference; always confirm exact specifications with the manufacturer for precision projects.
Choose the Right Wall Thickness:
Selecting the correct wall thickness is crucial for tube performance. Thicker walls are not always better, and thinner walls are not always weak. Understanding your project’s requirements—weight, vibration, welding, and material type—ensures safety, efficiency, and durability while keeping costs and weight optimized in 2026 designs.

1. Consider Load and Weight
The first factor in choosing wall thickness is the load the tube will carry. Furniture or decorative pieces may require thinner walls, while structural or automotive frames need thicker, stronger tubing. Correct thickness ensures the tube can safely handle expected stress without bending, sagging, or compromising structural integrity.
2. Assess Vibration and Movement
Tubes subjected to vibration or frequent movement need extra strength. Thicker walls reduce the risk of fatigue, cracking, or loosening over time. For machines, vehicles, or equipment frames, considering wall thickness for vibration resilience prevents maintenance issues and extends the life of both the tube and the assembly.
3. Evaluate Welding and Fabrication
Welding and fabrication impact wall thickness choice. Thicker tubes are easier to weld and align, while very thin tubes may burn through or deform. Fabricators must balance ease of joining with weight and cost, ensuring the tube maintains structural performance without unnecessary material usage.
4. Consider Weight Limitations
In projects where weight is critical, such as fitness equipment, automotive parts, or lightweight furniture, thinner walls may be preferable. Reducing wall thickness lowers overall weight while maintaining adequate strength, especially when using strong, modern materials like aluminum or stainless steel common in 2026 designs.
5. Match Material to Design Trends
Modern 2026 designs emphasize lightweight yet strong materials. Aluminum and stainless steel allow thinner walls without compromising strength, ideal for sleek, modular, and portable designs. Choosing wall thickness in harmony with material properties ensures durability, reduces costs, and meets both aesthetic and functional requirements for contemporary projects.
Metric vs Imperial Tube Sizes: What to Watch Out For
A common error is assuming metric and imperial tube sizes are interchangeable, but even slight differences matter. A 25 mm tube is not exactly the same as a 1-inch tube. Ignoring this can cause loose fittings, alignment issues, or welding gaps. Always verify the OD, wall thickness, and tolerance when mixing systems.
Also Read:
Confused about screw sizes? 👉 This Complete Guide 2026 explains everything you need to know—from diameter, length, and thread type to choosing the perfect screw for any project. Stop guessing and ensure a perfect fit every time. Read the full post now to make your DIY and professional work easier and precise!
Tube Size Tolerances Explained Simply
No tube is perfectly uniform; every tube has a tolerance, allowing minor variations in size. Modern 2026 charts clearly show OD and wall thickness tolerances. Tight tolerances are essential for precise assemblies, while looser tolerances are acceptable for structural work. Understanding tolerance is crucial, especially for CNC bending, automated welding, and high-precision fabrication.
Material Makes a Big Difference
Tube performance isn’t just about size; material plays a major role. The same OD and wall thickness can behave differently depending on whether the tube is steel, stainless steel, or aluminum. Considering the material ensures the tube meets strength, durability, corrosion resistance, and weight requirements for your specific project.
1- Steel Tubes
Steel tubes are known for their strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. While heavier than other materials, they provide excellent structural support. Their widespread use in construction and machinery highlights their reliability in projects where strength and load-bearing capacity are top priorities.
- Strong and durable
- Heavier
- Widely used in construction and machinery
2- Stainless Steel Tubes
Stainless steel tubes offer corrosion resistance and a clean, professional appearance. They are commonly used in food processing, medical devices, and architectural applications. Their ability to withstand moisture, chemicals, and environmental exposure makes them ideal for projects requiring hygiene, longevity, and aesthetic appeal.
- Corrosion resistant
- Cleaner appearance
- Common in food, medical, and architectural work
3- Aluminum Tubes
Aluminum tubes are lightweight and easy to work with, making them perfect for applications where portability or reduced weight is important. They are popular in automotive parts, fitness equipment, and lightweight structures. Despite being lighter, they maintain good strength and versatility for modern 2026 designs.
- Lightweight
- Easy to work with
- Popular in automotive and fitness equipment
Always check the tube chart specific to the material, not just the size.
How to Read a Tube Size Chart Without Stress
Reading tube size charts can seem confusing at first, but it becomes easy with a clear approach. Understanding the outside diameter, wall thickness, inside diameter, material compatibility, and tolerances helps you select the right tube confidently. With practice, charts become simple, accurate tools for any project.

Here’s a simple step-by-step approach:
- Identify the required outside diameter
- Choose a wall thickness based on strength needs
- Confirm the inside diameter
- Check material compatibility
- Review tolerances if precision matters
Once you do this a few times, charts become much less intimidating.
Mistakes People Still Make in 2026
Even experienced professionals can make errors when selecting tubes. Common mistakes include focusing on the inside diameter instead of the outside diameter, ignoring wall thickness, mixing pipe and tube standards, assuming sizes are universal, or overlooking tolerance limits. Being aware of these pitfalls ensures more accurate and reliable tube selection in 2026 projects.
- Ordering based on ID instead of OD
- Ignoring wall thickness
- Mixing pipe and tube standards
- Assuming sizes are universal across materials
- Not accounting for tolerance
Most of these mistakes are avoidable with one careful chart review.
Also Read:
Need to pick the right machine screw sizes? 👉 This guide is perfect for builders and DIYers, covering diameter, length, thread type, and compatibility. Learn how to choose screws that fit perfectly for any project. Stop guessing and avoid mistakes—read the full post now for easy, accurate screw selection!
Why Tube Size Charts Still Matter in the Age of Automation
Even with CAD software, CNC machines, and AI-assisted design tools becoming standard, tube size charts remain essential. Digital tools rely on accurate input, and entering the wrong size—even in software—leads to real-world errors. Charts provide a reliable reference for OD, ID, wall thickness, and tolerances, ensuring precision in fabrication, assembly, and design. For both professionals and DIYers, ignoring charts can result in misaligned parts, structural weaknesses, and costly rework, proving that traditional charts are still the backbone of accurate, modern tubing projects.
Final Thoughts: Tube Sizes Don’t Have to Be Complicated
Tube sizing may seem overwhelming, but once you understand outside diameter, wall thickness, and inside diameter, everything becomes clear. This 2026 Tube Size Chart guide simplifies selection for DIY projects and professional fabrication alike. Taking the time to read charts carefully, choose the right material, and account for tolerances saves time, money, and stress. Accuracy and intentional decision-making build confidence and ensure reliable, durable results. The key takeaway: slow down, check the chart, and make informed choices—small habits that pay off every single time.

