Brakes are the most crucial safety component in any vehicle, and at the heart of the braking system lies the brake rotor (also called brake disc). Rotors work with brake pads to create friction, allowing your vehicle to slow down or stop effectively. Over time, rotors wear down and need replacement, but before buying new ones, you need to know the correct brake rotor size for your vehicle.
That’s where a brake rotor size chart comes in handy. It provides essential measurements like diameter, thickness, and type of rotor that match your car, truck, or SUV. Whether you are a DIY car enthusiast, a mechanic, or simply want to understand your vehicle better, this guide will help you decode everything about brake rotor sizes.
Why Brake Rotor Size Matters
Brake rotors are not universal—different vehicles require different rotor dimensions. Choosing the wrong size can lead to poor braking performance, uneven wear, or even dangerous driving conditions. Here are some key reasons why rotor size matters:
Performance & Safety: Larger rotors provide better heat dissipation, reducing brake fade during heavy braking.
Compatibility: The caliper and pads are designed to fit a specific rotor size.
Durability: Using the correct rotor thickness ensures long-lasting brake performance.
Maintenance Cost: Correctly sized rotors reduce unnecessary wear and save money on brake repairs.
Key Measurements in a Brake Rotor Size Chart
When looking at a rotor size chart, you’ll typically see three important measurements:
Rotor Diameter (in mm or inches)
The overall width of the disc. Larger diameters are common in trucks, SUVs, and performance vehicles.
Rotor Thickness
This indicates how thick the disc is. Rotors have a minimum thickness specification; if worn below this, they must be replaced.
Bolt Pattern & Hub Size
The number of lug holes and the spacing between them. This must match your wheel hub.
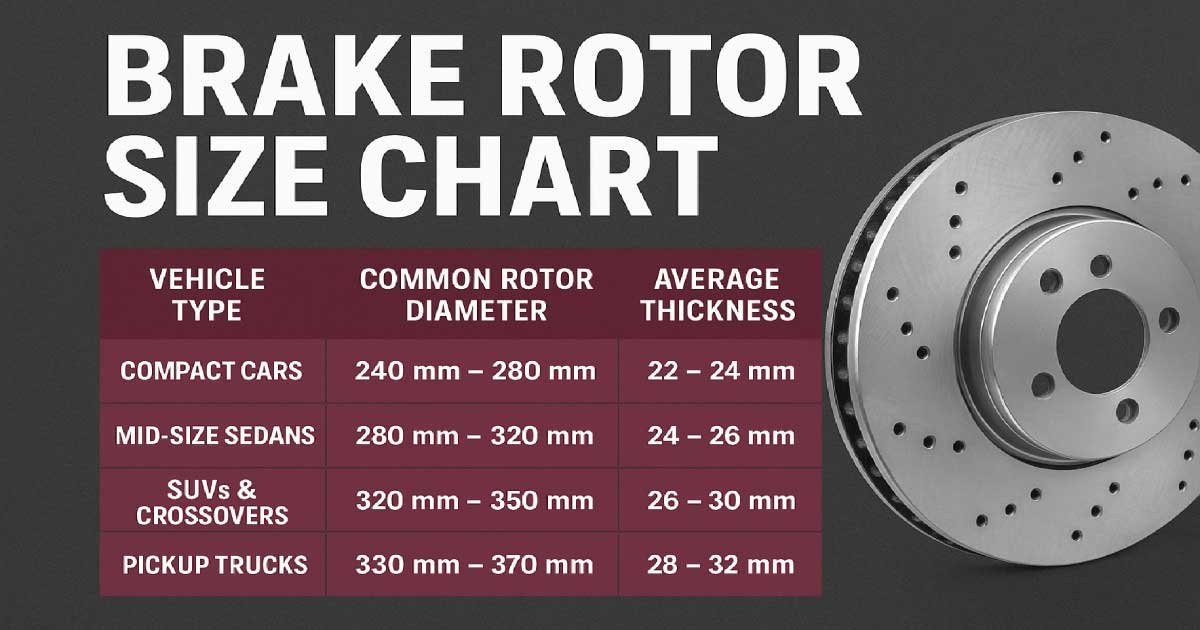
Brake Rotor Size Chart (General Reference)
Below is a general brake rotor size chart that shows common dimensions for different types of vehicles. Always verify with your car’s manual or manufacturer before purchasing.
| Vehicle Type | Common Rotor Diameter (Front) | Common Rotor Diameter (Rear) | Average Thickness (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Cars | 240 mm – 280 mm | 220 mm – 260 mm | 22 – 24 mm | Lightweight, economy-focused |
| Mid-Size Sedans | 280 mm – 320 mm | 260 mm – 300 mm | 24 – 26 mm | Balanced braking |
| SUVs & Crossovers | 320 mm – 350 mm | 300 mm – 330 mm | 26 – 30 mm | Designed for heavy loads |
| Pickup Trucks | 330 mm – 370 mm | 320 mm – 350 mm | 28 – 32 mm | Higher heat tolerance |
| Sports Cars | 340 mm – 400 mm | 320 mm – 380 mm | 30 – 34 mm | Performance-oriented |
| Heavy-Duty Vehicles | 380 mm – 430 mm | 350 mm – 400 mm | 32 – 36 mm | Built for towing & hauling |
Brake Rotor Size Chart Pdf
Download this comprehensive Brake Rotor Size Chart PDF to quickly find the correct rotor diameter, thickness, and bolt pattern for your vehicle. Includes general rotor sizes for cars, SUVs, trucks, and sports cars, as well as popular vehicle-specific rotor dimensions. Perfect for mechanics, DIY enthusiasts, and car owners to ensure proper brake rotor replacement and maintenance.
Types of Brake Rotors
Not all rotors are the same size, and not all are built the same way. Here are the most common types:
Solid Rotors
Found on economy cars and lighter vehicles. Best for everyday driving.
Vented Rotors
Two plates with air vents in between for better cooling. Common in trucks and SUVs.
Slotted Rotors
Have small grooves to improve grip and prevent gas buildup. Popular in performance cars.
Drilled Rotors
Holes drilled for better heat dissipation and water drainage. Used in high-performance or racing cars.
How to Measure Brake Rotor Size
If you’re unsure about your vehicle’s rotor size, here’s how you can measure it:
Remove the wheel to expose the rotor.
Measure the diameter across the rotor face.
Check the thickness with a caliper tool.
Count lug holes to confirm bolt pattern.
Tip: Always compare your measurement with the manufacturer’s minimum thickness specifications.
Brake Rotor Replacement Cost
One of the most common questions vehicle owners ask is: How much does brake rotor replacement cost?
On average:
Standard car rotors: $150 – $300 (for all four)
SUV & truck rotors: $250 – $500
High-performance rotors: $400 – $800
Labor costs can add another $100 – $250, depending on your location and vehicle type.
Signs You Need New Brake Rotors
Your rotors should be inspected regularly. Here are some signs that it’s time for replacement:
Vibration or pulsation while braking
Grinding or squealing noise
Visible grooves or scoring on the rotor surface
Increased stopping distance
Brake warning light
Brake Rotor Size Chart for Popular Vehicles
Here’s a sample list of common rotor sizes for popular car models. (Always check your exact year and trim for accuracy.)
| Vehicle Model | Front Rotor Size (mm) | Rear Rotor Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Toyota Camry | 296 mm | 281 mm |
| Honda Accord | 282 mm | 262 mm |
| Ford F-150 | 336 mm | 335 mm |
| Chevrolet Silverado | 330 mm | 345 mm |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee | 330 mm | 320 mm |
| BMW 3 Series | 312 mm | 300 mm |
| Mercedes C-Class | 320 mm | 300 mm |
| Dodge Charger (Performance) | 360 mm | 350 mm |
Brake Rotor Maintenance Tips
Check thickness regularly: Replace if below minimum spec.
Avoid aggressive driving: Hard braking reduces rotor life.
Use quality brake pads: Cheap pads can wear rotors faster.
Balance tires & wheels: Prevents uneven wear on rotors.
Keep rotors clean: Dirt and rust buildup affect performance.
OEM vs Aftermarket Brake Rotors
When replacing brake rotors, you’ll often face a choice between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket brake rotors.
OEM Rotors: Designed to match your vehicle’s exact specifications. They offer reliable performance but are usually more expensive. If you prioritize safety and don’t want to compromise, OEM is the safest bet.
Aftermarket Rotors: Available in a wide range of styles, such as drilled, slotted, or high-performance variants. They are often cheaper and can sometimes improve performance. However, quality varies by brand, so always buy from a trusted manufacturer.
This choice depends on your driving style. Daily drivers may prefer OEM, while enthusiasts and truck owners might lean toward aftermarket rotors with enhanced cooling or durability.
How Brake Rotor Size Affects Performance
Bigger isn’t always better, but rotor size does impact performance.
Larger rotors allow better heat dissipation, which is crucial during long drives, towing, or mountain driving.
Smaller rotors are lighter, helping fuel efficiency and handling in compact cars.
Performance cars often use oversized rotors with slotted or drilled surfaces for maximum braking power.
This is why understanding your brake rotor dimensions is key before upgrading or replacing.
Environmental Factors That Impact Rotor Life
Brake rotors don’t just wear out from usage—they are also affected by environment:
Rust and corrosion are common in humid or snowy regions.
Heat cycles in hot climates can cause warping over time.
Road salt and chemicals accelerate surface damage in winter.
Using coated rotors or stainless-steel variants can help extend rotor life in harsh climates.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Brake Rotor Size
Whether you drive a compact sedan, heavy-duty truck, or sports car, knowing your exact brake rotor size chart ensures optimal safety and performance. It’s not just about replacing worn-out parts—it’s about choosing the right rotors that match your driving style, environment, and vehicle type.
By paying attention to rotor diameter, thickness, and bolt pattern, you can avoid costly mistakes and keep your vehicle’s brake system efficient and reliable. When it comes to safety, never compromise—always invest in quality brake parts.
Also Read:
FAQs:
How do I know what size brake rotor I need?
You can find your brake rotor size by checking your vehicle’s owner manual or measuring the existing rotors. Key measurements include diameter, thickness, and bolt pattern. Online brake rotor size charts for your car model also help. Always match the rotor with your brake pads and calipers for proper fit and safety.
Can I replace brake rotors without replacing pads?
Technically, you can replace rotors without changing brake pads, but it’s not recommended. Worn pads can unevenly wear new rotors, causing vibration or reduced braking performance. For optimal safety and longevity, replace brake pads and rotors together. This ensures proper contact and prevents premature rotor wear.
What happens if my brake rotor is too thin?
If a brake rotor wears below its minimum thickness, it can overheat, warp, or crack under braking. Thin rotors reduce stopping power and increase braking distance, risking safety. Always check the rotor thickness specification in your manual and replace rotors when they reach the minimum limit to maintain proper braking performance.
How often should brake rotors be replaced?
Brake rotors usually last between 50,000 and 70,000 miles, depending on driving style, climate, and vehicle type. Aggressive braking, towing, or mountainous driving can wear rotors faster. Regular inspection for grooves, warping, or vibration during braking helps determine replacement intervals, keeping your braking system safe and efficient.
Can I upgrade to larger brake rotors?
Upgrading to larger rotors is possible and often improves braking performance by increasing heat dissipation. However, you must ensure your calipers, wheel size, and suspension can accommodate bigger rotors. Performance vehicles, trucks, or SUVs may benefit, but always check manufacturer guidelines or consult a mechanic before upgrading.
Are drilled or slotted rotors better than standard ones?
Drilled and slotted rotors offer better heat dissipation, improved braking in wet conditions, and reduced brake fade. Standard solid rotors are fine for daily driving. For performance cars, heavy-duty trucks, or enthusiasts, drilled or slotted rotors provide enhanced safety and efficiency, especially under extreme driving conditions or high temperatures.