Bricks are among the oldest and most reliable building materials, valued for their strength, durability, and versatility across centuries of construction. From ancient structures to modern architecture, bricks continue to play a vital role in creating safe and aesthetically pleasing buildings. Selecting the correct brick size is crucial, as it directly affects structural stability, bonding patterns, visual proportions, and overall cost efficiency.
Different projects require different brick dimensions depending on load-bearing needs and design intent. This guide explores standard brick dimensions, various brick types, regional size variations, and practical tips to support accurate planning, efficient material estimation, and successful construction execution.
Why Brick Size Matters
Choosing the right brick size is essential for both the strength and efficiency of a construction project. Brick dimensions influence structural stability, material usage, and overall design. Using the proper size ensures walls are durable, construction is cost-effective, and the final structure meets both aesthetic and functional requirements.
1-Wall Thickness and Structural Strength:
Brick size directly impacts wall thickness and the overall strength of a structure. Larger bricks can reduce the number of joints, increasing stability, while smaller bricks allow for more flexibility in design. Selecting the right brick size ensures walls can withstand load-bearing demands, resist environmental stress, and maintain structural integrity over time.
2-Mortar Usage:
The size of bricks affects how much mortar is required for construction. Smaller bricks increase the number of joints, leading to higher mortar consumption, while larger bricks reduce joint volume and save material. Choosing an appropriate brick size helps manage construction costs, minimize waste, and ensures consistent bonding for a long-lasting, durable wall.
3-Construction Speed:
Brick size influences the speed of construction. Larger bricks cover more area per unit, reducing the time needed for wall assembly, whereas smaller bricks require more placement and alignment effort. Selecting the optimal brick size allows builders to work efficiently, maintain accuracy, and complete projects on schedule without compromising quality.
4-Architectural Design and Aesthetics:
The dimensions of bricks affect the visual appeal and design flexibility of a structure. Smaller bricks allow for intricate patterns and decorative detailing, while larger bricks create a uniform, minimalist look. Choosing the right size ensures that architectural intentions are met, enhancing both the functionality and aesthetic value of the finished construction.
6-Cost of Material:
Brick size can influence overall material costs. Smaller bricks may require more units and additional mortar, increasing expenses, while larger bricks reduce the number needed and can lower labor costs. Selecting the right size helps balance material, labor, and time efficiency, ensuring that construction remains budget-friendly without compromising durability or quality.
Selecting the correct brick size ensures a balanced combination of durability and efficiency.
Standard Brick Dimensions
Bricks come in several standard sizes to meet building codes and construction needs. The most commonly used types are modular, standard, and queen size bricks. Each size is designed to provide consistent dimensions for walls, pavements, and other structures, ensuring uniformity, structural stability, and ease of installation.
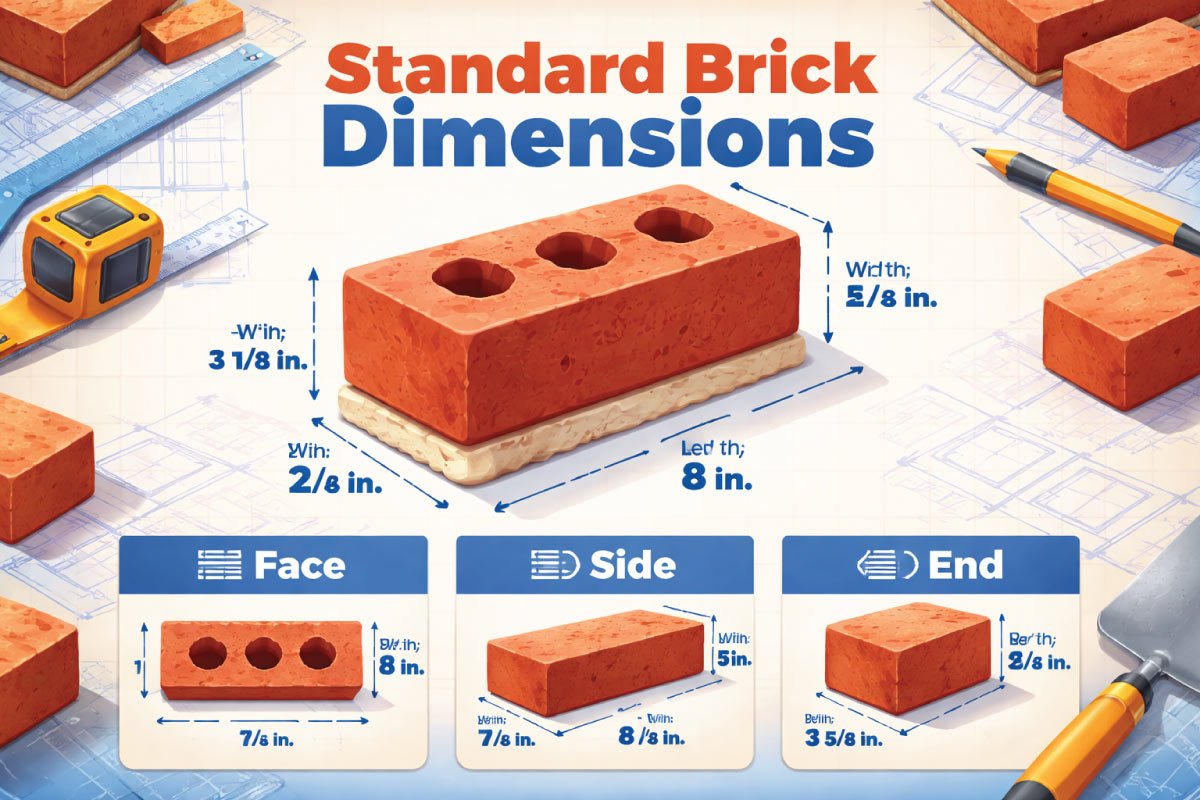
Modular Brick Size
Modular bricks are widely used in modern construction due to their standardized proportions, which simplify design, planning, and construction. Following a 4:2:1 length-to-width-to-height ratio, these bricks ensure consistent dimensions, reduce mortar use, and allow for faster, more efficient wall assembly while maintaining strength and uniformity.
Typical dimensions: 190 mm × 90 mm × 90 mm (length × width × height)
Standard Brick Size
Standard bricks are slightly larger than modular bricks, providing extra thickness for walls and enhanced structural strength. Their dimensions are typically 230 mm × 110 mm × 76 mm, making them suitable for load-bearing walls, partitions, and other construction applications where durability and stability are important.
Typical dimensions: 230 mm × 110 mm × 76 mm
Queen and King Brick Sizes
Larger bricks, such as queen and king bricks, are often used for architectural features and to reduce the number of mortar joints in a wall.
Queen Brick Dimensions: 230 mm × 110 mm × 90 mm
King Brick Dimensions: 230 mm × 114 mm × 90 mm
These sizes provide both visual impact and construction efficiency, making them ideal for special designs or structural needs.
Nominal vs Actual Brick Sizes
Understanding the difference between nominal and actual brick sizes is important for accurate construction planning. Nominal size accounts for both the brick and the mortar joint, while actual size refers to the brick’s physical dimensions alone. This distinction ensures proper alignment, accurate material estimation, and consistent wall construction.

1-Nominal Size
Nominal size includes the brick itself plus a standard mortar joint, usually 10 mm thick. For example, a standard brick’s nominal size is 240 mm × 115 mm × 75 mm, which helps in planning courses and calculating materials.
2-Actual Size
Actual size refers to the physical dimensions of the brick only, without any mortar. This is typically slightly smaller than the nominal size, allowing the mortar to fill gaps and ensure a strong, level structure.
Example: Standard brick nominal size is 240 mm × 115 mm × 75 mm, including mortar thickness.
Regional Brick Size Variations
Brick sizes differ around the world due to varying construction standards, local practices, and building requirements. Understanding these regional differences is important for architects, builders, and anyone sourcing bricks internationally, as it affects wall thickness, mortar usage, and structural design.
Brick Sizes in Different Countries
| Country | Standard Brick Size (mm) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 203 × 92 × 57 | Common modular size |
| UK | 215 × 102.5 × 65 | Modular brick, common in residential construction |
| India | 190 × 90 × 90 | Standard modular brick |
| Australia | 230 × 110 × 76 | Used for cavity walls |
| Canada | 190 × 90 × 57 | Smaller modular bricks for lightweight walls |
Types of Bricks Based on Material
Bricks are classified by the materials used in their production, which affects their strength, durability, and suitability for different construction applications. Choosing the right material ensures structural integrity, cost efficiency, and longevity of the building. Common types include clay, concrete, fly ash, and engineering bricks, each with specific properties.
1-Clay Bricks
Clay bricks are traditional building materials made from natural clay and fired in kilns. They are durable, fire-resistant, and provide good thermal insulation, making them ideal for general construction and decorative walls.
2-Concrete Bricks
Concrete bricks are made from cement, sand, and aggregates. They are strong, cost-effective, and suitable for large-scale construction projects. Their uniform size and shape make them easy to work with in walls and partitions.
3-Fly Ash Bricks
Fly ash bricks are lightweight and environmentally friendly, made from fly ash, cement, and water. They reduce construction weight and are ideal for non-load-bearing walls, offering good insulation and durability.
4-Engineering Bricks
Engineering bricks are high-strength, dense bricks with low water absorption. They are water-resistant and highly durable, making them suitable for foundations, retaining walls, and structures exposed to harsh conditions.
Bricks by Shape
Bricks come in a variety of shapes to meet different construction and design needs. From standard rectangular bricks for walls to specialty shapes like bullnose, coping, or interlocking bricks, each type serves a specific purpose. Choosing the right brick shape ensures structural integrity, aesthetic appeal, and efficient construction.
Rectangular bricks – Standard walls
Bullnose bricks – Rounded edges for corners
Coping bricks – Top of walls or parapets
Specialty bricks – L-shaped, perforated, or interlocking
Wall Thickness and Brick Layout
Brick size directly affects wall thickness and the choice of bond patterns in construction. Proper selection ensures structural stability, aesthetic appeal, and efficient use of materials. Different wall configurations, such as single, one-and-a-half, or double brick walls, are used depending on load requirements and design preferences.
1-Single Brick Wall
A single brick wall is typically 110 mm thick, consisting of one brick laid lengthwise. It is commonly used for partition walls or non-load-bearing structures where minimal thickness is sufficient.
2-One and a Half Brick Wall
A one-and-a-half brick wall measures 165 mm thick, combining strength and durability. It is suitable for load-bearing walls and provides better insulation compared to a single brick wall.
3-Double Brick Wall
A double brick wall has a thickness of 230 mm, offering maximum strength, stability, and thermal insulation. It is often used in exterior walls and heavy load-bearing structures.
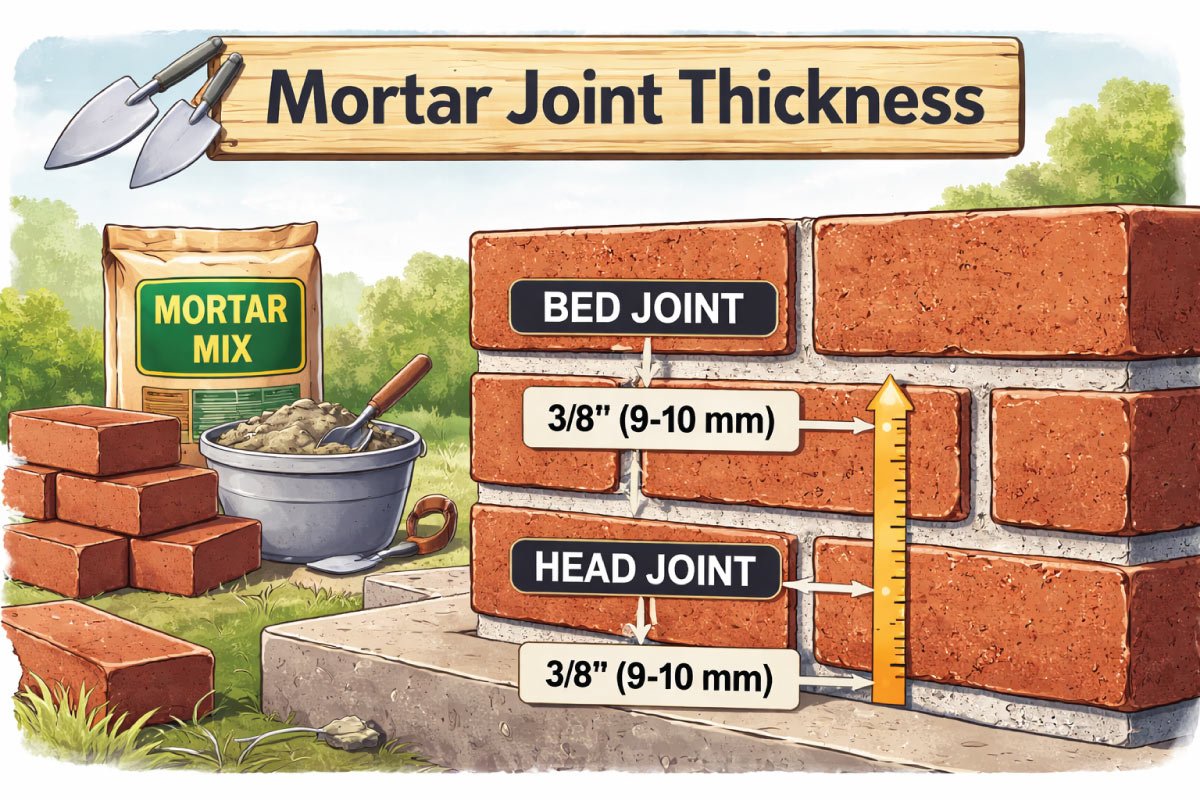
Mortar Joint Thickness
Mortar joint thickness plays a key role in wall construction, influencing overall height, structural strength, and the number of bricks required. Proper joint thickness ensures uniform load distribution, strong adhesion between bricks, and accurate alignment. The standard mortar joint thickness commonly used in construction is 10 mm.
Brick Count Per Square Meter
The number of bricks required per square meter depends on both the brick dimensions and the thickness of the mortar joints. Calculating the correct brick count helps plan material needs, control costs, and ensures consistent wall construction. Different brick types, such as standard, modular, king, or queen, will affect the quantity needed for each square meter.
Approximate Brick Count Per Square Meter
| Brick Type | Brick Size (mm) | Mortar Joint (mm) | Bricks per m² |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 230 × 110 × 76 | 10 | 50–55 |
| Modular | 190 × 90 × 90 | 10 | 55–60 |
| King | 230 × 114 × 90 | 10 | 45–50 |
| Queen | 230 × 110 × 90 | 10 | 48–52 |
Weight of Bricks
The weight of a brick depends on its size, material, and density, affecting handling, transportation, and overall wall load. Knowing the approximate weight helps in planning construction logistics, estimating structural load, and calculating the total number of bricks required for a project.
Standard clay brick: 2.5–3 kg
Modular brick: 2.2–2.5 kg
Concrete brick: 3–4 kg
Brick Weight by Type
| Brick Type | Size (mm) | Approximate Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard clay | 230 × 110 × 76 | 2.7 |
| Modular clay | 190 × 90 × 90 | 2.3 |
| Concrete | 230 × 110 × 76 | 3.2 |
| Fly ash | 230 × 110 × 75 | 2.1 |
Factors Affecting Brick Size Selection
Choosing the right brick size involves more than standard dimensions. Structural demands, aesthetic goals, mortar usage, and construction efficiency all play a role. Considering these factors ensures walls are strong, visually appealing, cost-effective, and quicker to build, helping achieve the right balance between durability, design, and project efficiency.
Structural requirements: Load-bearing walls need larger bricks
Aesthetic design: Size affects wall pattern and bond
Mortar consumption: Larger bricks reduce mortar usage
Construction speed: Bigger bricks cover more area, reducing labor
Brick Bond Patterns and Size Considerations
Brick bond patterns not only affect the structural strength of walls but also the visual appeal of a building. Choosing the right bond requires consideration of brick size and uniformity. Proper selection ensures stability, accurate alignment, and aesthetic consistency across walls and facades.
1-Stretcher Bond
Stretcher bond primarily uses standard bricks laid lengthwise along the wall. It is ideal for long walls and provides moderate strength while being easy to construct and cost-effective.
2-English Bond
English bond alternates rows of headers and stretchers, requiring standard brick sizes for proper alignment. This pattern provides excellent structural strength and is commonly used in load-bearing walls.
3-Flemish Bond
Flemish bond alternates headers and stretchers in each course, demanding uniform brick sizes for precise alignment. It is often chosen for its aesthetic appeal as well as structural stability.
4-Stack Bond
Stack bond involves stacking bricks directly on top of each other, typically using modular bricks. It is favored in modern designs for visual effect but provides less structural strength compared to traditional bonds.
Also Read:
Special Considerations for Custom Bricks
Custom bricks offer flexibility for projects that demand unique designs or specific architectural features. They can help reduce mortar joints, match historical structures, or provide distinct textures and shapes. Considering these options allows builders and designers to achieve both functional and aesthetic goals while maintaining structural integrity.

Fit unique architectural designs
Reduce mortar joints
Match historical structures
Provide unique textures or shapes
Also Read:
Tips for Accurate Brick Estimation
Accurate brick estimation is essential to avoid material shortages, reduce costs, and prevent construction delays. Careful measurement, proper brick selection, and allowance for breakage ensure smooth project execution. Following simple estimation tips helps achieve precise material planning and efficient construction.
Environmental Considerations in Brick Sizing
Brick size and type can impact a project’s environmental footprint. Smaller, modular bricks reduce shipping weight and material use, while eco-friendly options like fly ash or compressed bricks lower carbon emissions. Considering these factors supports sustainable construction practices without compromising structural strength or design quality.
Maintenance and Durability Based on Size
Brick size influences both the durability of a wall and the ease of maintenance. Larger bricks can reduce the number of joints, minimizing potential water infiltration, while standard-sized bricks are easier to handle and replace, making repairs simpler and more efficient.
1-Impact of Larger Bricks
Using larger bricks reduces the total number of joints in a wall. Fewer joints mean less exposure to moisture, improving water resistance and long-term durability of the structure.
2-Advantages of Standard Bricks
Standard-sized bricks are easier to replace individually during maintenance. Their uniform dimensions allow for straightforward repairs without affecting surrounding bricks, ensuring longevity and reducing labor costs.
Also Read:

Final Thoughts
Understanding brick sizes is crucial for construction efficiency, aesthetics, and structural integrity. This brick size guide provides all the necessary information on standard, modular, and custom bricks, along with tables for size, weight, and brick count to help engineers, builders, and DIY enthusiasts make informed decisions.
Using the right brick size ensures strong walls, reduced costs, and faster construction.
Also Read:

