Fuses are small but critical safety devices used in electrical and electronic systems to protect circuits from overcurrent, short circuits, and electrical faults.
Choosing the correct fuse size is essential because an undersized fuse may blow unnecessarily, while an oversized fuse can fail to protect equipment, leading to overheating, fire risks, or component damage.
This fuse size guide explains fuse ratings, types, selection methods, and practical examples to help beginners and professionals make the right choice.
What Is a Fuse and How Does It Work?
A fuse is a sacrificial electrical component designed to interrupt current flow when the current exceeds a safe limit.
Inside the fuse is a metal element that melts when excessive current passes through it. Once melted, the circuit opens and stops the flow of electricity.
Fuses are widely used in household wiring, automotive systems, industrial machines, and electronic devices because they are simple, reliable, and cost-effective.
Why Fuse Size Matters
Fuse size is critical for electrical safety and system performance. A fuse rated too low may blow under normal operation, causing unnecessary downtime,
while an oversized fuse might fail to interrupt dangerous currents, risking equipment damage or fire.
Correct fuse sizing balances protection and reliability, ensuring both safe operation and uninterrupted functionality.
1. Prevents Equipment Damage
The correct fuse size ensures that electrical equipment is protected from excessive current.
Underrated fuses may trip unnecessarily, while overrated fuses can allow currents to exceed safe levels, damaging wiring, motors, or sensitive electronics.
Proper fuse selection maintains equipment integrity, reduces repair costs, and extends the lifespan of devices and industrial machinery.
2. Ensures Personal Safety
Fuses protect people from electrical hazards. If a fuse fails to blow during a fault, exposed wires or overheated circuits may create fire risks or electric shocks.
Correct sizing ensures that overcurrent conditions are interrupted promptly, minimizing the potential for injury,
And maintaining compliance with safety standards in residential, commercial, or industrial electrical systems.
3. Prevents Nuisance Blowing
A fuse rated too low may blow frequently during normal operation, causing repeated interruptions.
This is especially common in circuits with startup surges, such as motors or HVAC systems.
Properly sized fuses tolerate typical operating currents while still providing protection, reducing downtime, maintenance effort, and frustration from unnecessary fuse replacements.
4. Maintains Circuit Integrity
Properly sized fuses help preserve the integrity of wiring and components.
By limiting the current to safe levels, fuses prevent overheating, insulation damage, and component failure.
Maintaining circuit integrity ensures reliable performance, reduces the risk of cascading failures, and contributes to overall system efficiency in both household and industrial electrical installations.
5. Supports System Reliability
Correct fuse sizing contributes to predictable and reliable system operation.
Electrical systems function efficiently when overcurrent protection is calibrated for normal and peak loads.
Oversized fuses compromise protection, while undersized fuses cause unnecessary interruptions.
Properly chosen fuses help ensure consistent system uptime, operational continuity, and equipment availability.
6. Compliance with Standards
Fuse selection is often dictated by electrical codes and manufacturer recommendations.
Using a fuse outside the recommended rating can violate safety standards, void warranties, and increase liability.
Correctly sized fuses ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, maintain certification for equipment, and provide peace of mind that systems operate safely and legally.
Understanding Fuse Ratings
Fuse ratings describe the electrical limits within which a fuse can operate safely.
The most important ratings include current rating (amperes), voltage rating (volts), interrupting capacity, and time-current characteristics.
Understanding these ratings helps in selecting the correct fuse for a specific application.
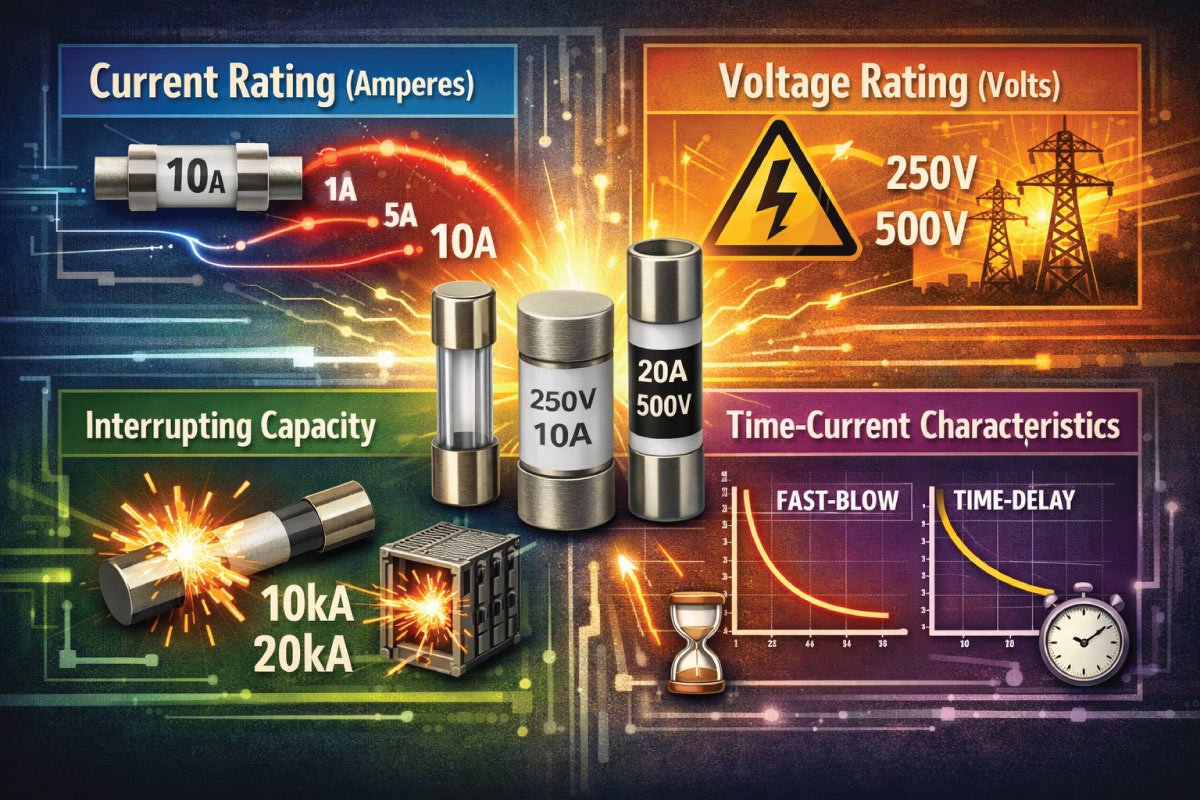
Fuse Current Rating Explained
The current rating of a fuse indicates the maximum current it can carry continuously without blowing.
It is measured in amperes (A). A fuse should typically be rated slightly higher than the normal operating current of the circuit.
This prevents nuisance blowing while still offering protection during overcurrent conditions.
Common Fuse Current Ratings and Typical Uses
| Fuse Rating (A) | Typical Application |
|---|---|
| 0.5 – 2 A | Small electronics, chargers |
| 3 – 5 A | Lighting circuits, small appliances |
| 7.5 – 10 A | Automotive accessories |
| 15 – 20 A | Household appliances |
| 25 – 30 A | Power tools, HVAC components |
Fuse Voltage Rating
The voltage rating of a fuse is the maximum voltage it can safely interrupt without arcing.
It is crucial to select a fuse with a voltage rating equal to or higher than the circuit voltage.
Using a fuse with a lower voltage rating can result in dangerous arcing and failure to properly interrupt the circuit.
Fuse Voltage Ratings and Applications
| Voltage Rating | Common Applications |
| 32 V | Automotive and low-voltage electronics |
| 125 V | Consumer electronics |
| 250 V | Household AC circuits |
| 500 V+ | Industrial and high-power systems |
Fast-Blow vs Slow-Blow Fuses
Fuses are classified based on their response speed to overcurrent conditions.
Fast-blow fuses act immediately to protect sensitive electronics from damage, while slow-blow fuses tolerate temporary surges, such as motor startups, without tripping.
Choosing the correct type ensures circuit protection, prevents unnecessary downtime, and extends the lifespan of both equipment and wiring.
Fast-Blow vs Slow-Blow Fuses – Key Differences
| Feature | Fast-Blow Fuse | Slow-Blow Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Opens instantly when rated current is exceeded | Delayed response, tolerates short surges |
| Surge Tolerance | Low – trips on minor overcurrent | High – withstands inrush currents |
| Typical Applications | Sensitive electronics like computers, LEDs | Motors, transformers, inductive loads |
| Protection Focus | Prevents immediate damage | Protects against sustained overloads while allowing temporary spikes |
| Advantages | Quick protection, precise | Reduces nuisance blowing, suitable for high inrush currents |
| Disadvantages | May blow unnecessarily during surges | Slower response may risk slight overcurrent exposure |
Comparison of Fast-Blow and Slow-Blow Fuses
Fast-blow and slow-blow fuses serve different roles in electrical circuits. Understanding their characteristics ensures proper protection of devices and equipment.
Fast-blow fuses react instantly to overcurrent, ideal for sensitive electronics, while slow-blow fuses tolerate temporary surges, making them suitable for motors and transformers.
Correct selection prevents damage and improves circuit reliability.
| Feature | Fast-Blow Fuse | Slow-Blow Fuse |
| Response Time | Instant | Delayed |
| Surge Tolerance | Low | High |
| Typical Use | Electronics | Motors, transformers |
Fuse Size Calculation Method
To calculate the correct fuse size, first determine the normal operating current of the circuit.
Then multiply this value by a safety factor, usually between 1.25 and 1.5. This ensures the fuse can handle normal operation while still protecting against faults.

Example: If a device draws 8 A continuously, a suitable fuse size would be: 8 A × 1.25 = 10 A fuse
This method is commonly used in residential, automotive, and industrial applications.
Automotive Fuse Size Guide
Automotive fuses protect vehicle electrical circuits from overcurrent and short circuits.
Designed for 12 V or 24 V systems, they are color-coded for easy identification.
Choosing the correct fuse size prevents wiring damage, ensures safe operation of electronics, and maintains vehicle reliability.
Proper sizing is essential for both standard and high-power automotive components.
1. Headlights and Lighting Circuits
Fuses in automotive lighting protect headlights, taillights, and interior lights from overcurrent.
Selecting the correct amperage ensures bulbs operate safely without blowing fuses unnecessarily.
Properly sized fuses prevent wiring overheating, preserve circuit integrity, and maintain visibility and safety while driving, especially during night or adverse weather conditions.
2. Infotainment Systems
Automotive fuses safeguard radios, infotainment displays, and navigation systems.
Correct fuse sizing prevents damage to sensitive electronics during power surges or short circuits.
Using the recommended amperage protects both the wiring and connected devices, ensuring reliable performance and uninterrupted audio, video, and connectivity features inside the vehicle.
3. Air Conditioning and Climate Control
High-current fuses protect HVAC systems, including compressors, fans, and blowers.
Proper fuse selection ensures the climate control system operates safely under varying electrical loads.
Undersized fuses may blow during normal operation, while oversized fuses risk wiring damage. Correctly rated fuses maintain system efficiency and passenger comfort.
4. Power Accessories
Fuses protect additional power accessories such as electric windows, seat heaters, and charging ports.
Correct amperage ensures these circuits operate safely without damaging wiring or the vehicle’s main electrical system.
Properly sized fuses maintain both accessory performance and overall vehicle electrical safety.
Automotive Blade Fuse Color and Rating Chart
Automotive blade fuses use color-coding to indicate their current rating, simplifying identification and replacement.
Each color corresponds to a specific ampere value, ensuring drivers select the correct fuse for circuits like headlights, radios, and power accessories.
Understanding this system prevents overcurrent damage, protects wiring, and maintains reliable operation of automotive electrical components.
| Color | Rating (A) |
| Tan | 5 A |
| Brown | 7.5 A |
| Red | 10 A |
| Blue | 15 A |
| Yellow | 20 A |
| Green | 30 A |
Household Fuse Size Guide
In residential electrical systems, selecting the correct fuse size is essential for safety and efficient operation.
Fuse ratings must align with both circuit load and wire gauge. Smaller fuses are used for lighting circuits,
while higher-rated fuses protect appliances like air conditioners and kitchen equipment.
Proper matching prevents overheating and reduces the risk of electrical hazards.

1. Lighting Circuits
Residential lighting circuits typically use low-current fuses, often 5–15 A depending on wire gauge and fixture load.
These fuses protect wiring from overheating and prevent fire hazards. Correctly sized fuses ensure stable operation of lights,
while minimizing nuisance trips, providing reliable protection for switches, outlets, and connected fixtures throughout the home.
2. Kitchen Appliances and Air Conditioners
High-power appliances such as ovens, refrigerators, and air conditioners require fuses with higher ratings, often 15–30 A or more.
Properly sized fuses prevent excessive current from damaging appliance wiring and components while maintaining overall household electrical safety.
Matching fuse ratings with appliance load and wire gauge ensures both functionality and protection against overloads.
Industrial Fuse Sizes and Applications
Industrial fuses are critical for protecting high-current, high-voltage circuits in demanding environments.
They safeguard motor control centers, power distribution systems, and heavy machinery by interrupting fault currents before damage occurs.
Selecting the correct fuse size ensures operational reliability, reduces downtime, and protects both equipment and personnel in industrial facilities where safety and continuity are paramount.
1. Motor Control Centers (MCCs)
Fuses in motor control centers protect motors, contactors, and associated circuits from overloads and short circuits.
Correct fuse sizing prevents winding damage and ensures safe motor operation.
High interrupting capacity allows the fuse to handle fault currents effectively, maintaining equipment reliability and protecting operators from electrical hazards in heavy industrial operations.
2. Power Distribution Panels
Industrial fuses safeguard transformers, branch circuits, and feeders in distribution panels.
Proper selection ensures overcurrent protection without unnecessary downtime. These fuses prevent damage to connected equipment while maintaining continuity in the electrical system.
High-rated industrial fuses accommodate large currents and fault conditions common in factories and commercial facilities.
3. Heavy Machinery
Fuses protect heavy industrial machinery like presses, crushers, and conveyors.
They prevent electrical damage caused by overloads or short circuits, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
Correctly rated fuses also account for startup surges, protecting motors and control systems.
This reduces downtime, maintenance costs, and equipment failure in high-demand industrial settings.
4. Transformers
Industrial fuses protect transformer primary and secondary circuits from short circuits and overcurrent events.
Proper sizing prevents catastrophic damage, enhances safety, and ensures continued operation under normal load.
High interrupting capacity fuses isolate faults quickly, maintaining system reliability and extending transformer lifespan in industrial and commercial power distribution systems.
5. Industrial HVAC Systems
High-power HVAC systems in factories and large buildings require fuses to safeguard compressors, fans, and motors.
Correctly sized fuses prevent electrical damage and overheating while accommodating startup currents.
They maintain smooth operation, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure personnel safety in high-demand industrial HVAC applications.
6. Welding Equipment
Industrial fuses protect welding machines from overloads and short circuits. Correct fuse selection prevents damage to internal circuits and wiring while ensuring operator safety.
They also handle high startup currents common in welding operations, maintaining reliable performance and minimizing
the risk of equipment downtime in industrial fabrication or construction environments.
7. UPS and Backup Power Systems
Fuses in UPS units and backup generators safeguard batteries, inverters, and distribution circuits.
They interrupt high currents during faults, preventing damage and ensuring operational continuity.
Properly sized fuses maintain system reliability, allowing emergency power to function safely during outages in industrial facilities, data centers, or critical operations.
8. Robotic and Automated Systems
Industrial fuses protect drives, motors, and controllers in automated production lines and robotic systems.
Properly sized fuses prevent overcurrent damage, reduce downtime, and maintain production efficiency.
They accommodate startup currents and fault conditions, ensuring operational safety and reliable performance in high-speed, automated industrial environments.
Fuse Size vs Wire Gauge Relationship
Selecting the correct fuse size in relation to wire gauge is essential for safe electrical operation.
The fuse protects the wire from overheating, not just the device. Using a fuse with a higher rating than the wire can handle may cause,
the wire to overheat or catch fire before the fuse blows. Proper coordination ensures both wire and circuit safety.
Fuse Size vs Wire Gauge
| Wire Gauge (AWG / mm²) | Recommended Fuse Rating | Purpose | Risk of Incorrect Fuse | Tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 AWG / 2.0 mm² | 15 A | Protects wire from overheating | Overcurrent may melt wire | Match fuse rating ≤ wire capacity |
| 12 AWG / 3.0 mm² | 20 A | Safe for typical household circuits | Exceeding fuse rating can cause fire | Check insulation type & temperature |
| 10 AWG / 5.0 mm² | 30 A | Protects wire in heavy-duty circuits | Wire may overheat before fuse blows | Confirm wire is copper or aluminum rated |
| 8 AWG / 8.0 mm² | 40–50 A | High-power applications | Using lower fuse may cause nuisance blowing | Verify circuit load requirements |
| 6 AWG / 13 mm² | 60–70 A | Industrial machinery & HVAC | Undersized fuse may trip frequently |
Discover More:
Common Mistakes When Choosing Fuse Sizes
Choosing the correct fuse size is crucial for electrical safety and equipment protection.
Common mistakes can lead to fire hazards, equipment damage, or personal injury.
Understanding the proper rating, type, and application prevents these risks.
Avoid shortcuts or assumptions when replacing fuses to ensure circuits remain protected and operate reliably.

Replacing a blown fuse with a higher-rated fuse to avoid repeated blowing.
Ignoring the voltage rating of the fuse.
Using the wrong fuse type (fast-blow vs slow-blow) for the application.
Installing fuses that don’t match manufacturer specifications.
Reusing damaged or melted fuses.
Bypassing a fuse with wire or metal objects.
Using fuses with incorrect physical size, causing poor fit.
Failing to check circuit load conditions before selecting a fuse.
Discover More:
Safety Tips for Fuse Selection
Selecting and handling fuses safely is critical to prevent electrical hazards, equipment damage, and personal injury.
Using the correct fuse size and rating ensures proper circuit protection.
Always follow manufacturer guidelines, disconnect power before replacement, and avoid unsafe practices.
Proper safety measures help maintain both electrical system reliability and personal safety.
Always disconnect power before inspecting or replacing a fuse.
Use the manufacturer’s recommended fuse rating for the circuit.
Keep a stock of correct-size spare fuses for quick replacement.
Never bypass a fuse with wire, metal, or other conductive objects.
Inspect fuses for visible damage or discoloration before use.
Avoid mixing different types or ratings in the same circuit.
Ensure the fuse holder or socket is clean and secure.
Replace blown fuses immediately; do not leave circuits unprotected.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct fuse size is essential for electrical safety, reliability, and performance.
By understanding fuse ratings, types, and calculation methods, you can confidently choose the right fuse for automotive, household, or industrial applications.
This fuse size guide serves as a practical reference to help you avoid common mistakes and ensure long-lasting protection for your electrical systems.
A properly sized fuse is a small investment that provides big protection, making it a fundamental component of any safe electrical setup.
Discover More:

