Manufacturing equipment includes machinery, tools, and automated systems used in production, assembly, and packaging. Regular maintenance ensures efficiency and longevity.
Introduction
Did you know that the global manufacturing industry relies on over 60 million pieces of machinery to keep production running smoothly? From small-scale factories to multinational corporations, manufacturing equipment is the backbone of modern industry, responsible for turning raw materials into the products we use every day. Without this machinery, the efficiency, safety, and profitability of industries would drastically diminish.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the world of manufacturing equipment—covering everything from what it is, its importance in different industries, the various types, and their uses. We’ll also explore best practices for maintaining these critical tools and look at the future trends shaping the manufacturing landscape.
What is Manufacturing Equipment?
Manufacturing equipment refers to the machinery, tools, and systems used in the production of goods. This equipment facilitates various processes in industries ranging from automotive and electronics to food and pharmaceuticals. Whether it’s cutting metal, assembling parts, or packaging finished products, manufacturing equipment is essential for transforming raw materials into end products efficiently and with precision.

Importance of Manufacturing Equipment
The importance of manufacturing equipment cannot be overstated. It increases productivity, reduces labor costs, enhances product quality, and ensures safety standards. In high-demand industries, where precision and speed are critical, manufacturing equipment enables companies to meet tight deadlines while maintaining consistency. Equipment like CNC machines, robots, and quality control systems play key roles in streamlining operations, minimizing human error, and delivering higher outputs.
Machines in Manufacturing
Machines in manufacturing are essential for improving efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. They automate manual tasks, increase production speed, and maintain product quality. Modern industries rely on machines like CNC machines, lathes, milling machines, and robots to produce components precisely and consistently, making mass production faster and more reliable.
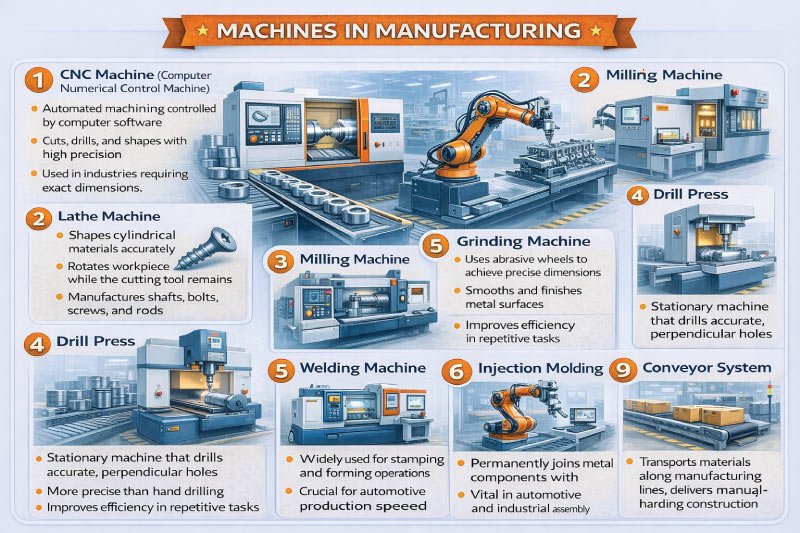
1. CNC Machine (Computer Numerical Control Machine)
CNC machines are automated devices controlled by computer software. They can cut, drill, and shape metal, plastic, and wood with high precision. CNC machines reduce material waste, handle repetitive tasks efficiently, and are widely used in industries requiring exact dimensions and complex designs.
2. Lathe Machine
Lathe machines are used to shape cylindrical materials. The workpiece rotates while the cutting tool remains stationary, allowing precise shaping. Lathes are commonly used to manufacture shafts, bolts, screws, and rods. They work effectively with both metal and wood, making them versatile in manufacturing.
3. Milling Machine
Milling machines remove material to create flat, angled, or curved surfaces. A rotating cutter and movable table allow precise shaping of components. They are essential for making slots, grooves, and complex parts in metal and plastic manufacturing, providing accurate and repeatable results.
4. Drill Press
A drill press is a stationary machine used to create accurate holes in materials. It ensures perpendicular and uniform holes, making it more precise than hand drilling. Drill presses are commonly used for woodworking, metalworking, and plastic fabrication, improving efficiency and consistency in repetitive tasks.
5. Grinding Machine
Grinding machines use abrasive wheels to smooth surfaces and achieve precise dimensions. They are used after cutting or shaping to provide a fine finish. Grinding enhances durability, accuracy, and performance of metal components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing.
6. Press Machine
Press machines apply mechanical force to bend, punch, or shape metal sheets. They are widely used for stamping and forming operations. Press machines are crucial for sheet metal fabrication, automotive panels, and industrial parts, as they ensure speed, accuracy, and consistent quality.
7. Welding Machine
Welding machines join metal components permanently using heat or pressure. They are vital in construction, automotive, and industrial assembly for creating strong, durable joints. Welding machines can work with steel, aluminum, and iron, making them essential in manufacturing structural and machinery parts.
8. Injection Molding Machine
Injection molding machines shape plastics by injecting molten material into molds. They are widely used for producing plastic bottles, containers, automotive components, and consumer products. Injection molding provides high precision, fast production rates, and consistent quality for large-scale plastic manufacturing.
9. Assembly Robot
Assembly robots perform automated assembly tasks, including positioning and fastening parts. They reduce labor costs, increase production speed, and ensure consistent quality. These robots are widely used in electronics, automotive, and industrial manufacturing for repetitive or precise assembly operations.
10. Conveyor System
Conveyor systems transport materials and products from one point to another in manufacturing lines. They reduce manual handling, improve workflow efficiency, and enhance safety. Conveyors are commonly used in factories, warehouses, and packaging units to streamline production and material movement.
11. Shearing Machine
Shearing machines cut metal sheets in straight lines using sharp blades. They are widely used in sheet metal fabrication, automotive body panel production, and industrial component manufacturing. Shearing machines ensure accurate, fast, and clean cuts for high-quality results.
12. EDM Machine (Electrical Discharge Machining)
EDM machines shape electrically conductive materials using controlled electrical sparks. They remove material precisely without physical contact, allowing the creation of complex parts, molds, and dies. EDM machines are ideal for components where traditional cutting tools cannot achieve the required precision.
Types of Manufacturing Equipment
The vast array of manufacturing equipment can be grouped into several categories based on their functionality and use. Below are the most common types:
1. Machinery
Machinery refers to larger, more complex equipment used to carry out specific production tasks. Some of the most common types of machinery include:
CNC Machines (Computer Numerical Control): CNC machines are automated machines that use pre-programmed software to control the movement of tools and machinery. They are used for cutting, drilling, and shaping materials like metal, plastic, and wood.
Lathes: Lathes are versatile machines used for shaping materials by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool. They are commonly used in metalworking, woodworking, and glassworking.
Milling Machines: These machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, creating intricate shapes and designs. Milling machines are crucial in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
2. Tools
While machinery handles large-scale production tasks, tools are the smaller, often handheld, devices used for more detailed or manual work. Examples include:
Hand Tools: Wrenches, hammers, and pliers are commonly used in various stages of production, assembly, and maintenance.
Power Tools: Drills, saws, and grinders powered by electricity or batteries make tasks like cutting, drilling, and fastening more efficient and less labor-intensive.
3. Automation Equipment
Automation has revolutionized manufacturing, allowing companies to increase output, reduce errors, and improve safety. Key automation equipment includes:
Robotics: Industrial robots handle repetitive tasks such as welding, painting, assembly, and material handling. Their precision and speed make them invaluable in sectors like automotive and electronics.
Conveyor Systems: Conveyor belts and roller systems automate the movement of goods throughout the production process, minimizing human intervention and increasing efficiency.
4. Quality Control Equipment
Ensuring that products meet required standards is a critical aspect of manufacturing, and specialized equipment is designed for this purpose. Key quality control equipment includes:
Inspection Machines: Optical and X-ray inspection machines are used to identify defects or inconsistencies in products before they reach the customer.
Testing Equipment: Devices like tensile testers and hardness testers measure the strength, flexibility, and durability of materials, ensuring they meet industry standards.
Uses of Manufacturing Equipment
Manufacturing equipment is utilized throughout the entire production process, from raw material handling to final packaging. Here’s how this equipment is used in various stages:
1. Production
The primary function of manufacturing equipment is to transform raw materials into finished products. Machinery like CNC machines, lathes, and milling machines is essential for shaping, cutting, and assembling materials. Automated systems, like robotics, assist in handling repetitive tasks, improving speed and consistency.
For example, in the automotive industry, robots are widely used for welding car bodies, while CNC machines are used to produce engine parts with extreme precision.
2. Assembly
Once the individual parts are produced, assembly equipment plays a crucial role in putting them together. Automated assembly lines with robotic arms, pick-and-place systems, and conveyor belts help streamline the process. For instance, in the electronics industry, pick-and-place machines assemble components onto circuit boards with high accuracy.
3. Packaging
After production and assembly, products need to be packaged for distribution. Packaging equipment like sealing machines, labeling systems, and shrink-wrapping machines automate the process, ensuring products are packed securely and efficiently. In industries like food and beverage, this equipment is essential for maintaining hygiene standards and ensuring the product reaches consumers in optimal condition.
4. Maintenance
Even the equipment used in production requires maintenance to ensure longevity and performance. Maintenance equipment like lubrication systems, diagnostic tools, and cleaning devices help keep machines in top condition. In industries where machinery runs continuously, like pharmaceuticals or electronics, regular maintenance prevents costly downtime.
Best Practices for Maintaining Manufacturing Equipment
To ensure manufacturing equipment operates efficiently and lasts for years, companies need to follow best practices in maintenance. Below are key strategies for effective equipment upkeep:
1. Regular Inspections
Routine inspections are vital for identifying potential issues before they escalate into major problems. This involves checking for wear and tear, ensuring all parts are functioning correctly, and making adjustments where needed. Scheduling regular inspections reduces the risk of unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
2. Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves conducting regular maintenance tasks, such as cleaning, lubricating, and replacing worn-out parts, before issues arise. It’s a proactive approach that extends the life of equipment and improves efficiency. Preventive maintenance schedules should be strictly followed to keep machinery running at optimal levels.
3. Corrective Maintenance
Even with the best preventive measures, equipment can still break down. Corrective maintenance involves repairing or replacing malfunctioning parts after a problem occurs. Quick and efficient corrective maintenance is crucial to minimize downtime and get production back on track.
4. Training
Proper training is critical for those who operate and maintain manufacturing equipment. Employees should be well-versed in how to handle equipment safely, perform routine maintenance, and identify early signs of problems. Investing in training helps avoid human errors that could lead to equipment failure or safety risks.
Discover the various manufacturing process types in our detailed guide! Learn how each process works, from batch production to continuous flow, with real-world examples to illustrate their applications. Read more to enhance your understanding of manufacturing operations and efficiency!
Future Trends in Manufacturing Equipment
As technology continues to evolve, the future of manufacturing equipment is bright, with several trends shaping the industry:
1. Technological Advancements
Emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and 3D printing are transforming how manufacturing equipment is used. IoT-enabled machines provide real-time data that can be analyzed to optimize performance and predict failures. AI helps automate complex tasks and improve precision, while 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping and on-demand production.
2. Sustainability
As industries strive to reduce their environmental impact, sustainable manufacturing equipment is gaining importance. This includes machines that use less energy, produce less waste, and are made from eco-friendly materials. Companies are also adopting recycling practices and reusing resources to minimize waste in production.
3. Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing, often referred to as Industry 4.0, integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing to create fully connected and intelligent production systems. These systems allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized workflows, leading to greater efficiency, reduced costs, and improved product quality.
Learn all about manufacturing processes in our comprehensive guide! Explore the methods that transform raw materials into finished products, with key insights into each step. Read more to deepen your knowledge of how modern manufacturing drives innovation and productivity!
Conclusion
Manufacturing equipment is the lifeblood of modern industry, enabling companies to produce goods efficiently, safely, and cost-effectively. From CNC machines and robots to hand tools and quality control devices, the right equipment ensures high productivity and product quality.
By following best practices for maintenance, such as regular inspections and preventive care, businesses can extend the life of their equipment and avoid costly downtime. As the manufacturing landscape evolves with technological advancements and a focus on sustainability, staying updated with future trends will be key to staying competitive.