PVC pipes are everywhere—behind walls, under floors, in gardens, factories, farms, and massive infrastructure projects. Yet most people only notice them when something goes wrong. A leak. A blockage. A broken joint. That’s usually the moment we ask: What kind of PVC pipe is this, and was it the right one to begin with?
In 2026, PVC piping has evolved far beyond basic plumbing. New materials, improved pressure ratings, eco-friendly formulations, and standardized sizing systems have made PVC one of the most reliable piping solutions worldwide. Whether you’re a homeowner, engineer, contractor, or simply curious, understanding PVC pipe types, sizes, and materials helps you make smarter, longer-lasting decisions.
This guide breaks everything down clearly—no jargon overload, no confusion—just practical knowledge that actually helps.
What Is PVC Pipe and Why It’s Still Dominating in 2026
PVC stands for Polyvinyl Chloride, a synthetic plastic polymer known for being lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant, and highly cost-effective. Unlike metal pipes, PVC does not rust, scale, or chemically react with water, which helps maintain water quality. These qualities make PVC pipes reliable, long-lasting, and widely used in plumbing and industrial systems.
But the real reason PVC remains dominant in 2026 is adaptability.
PVC pipes can handle:
- Residential plumbing
- Industrial chemical flow
- Agricultural irrigation
- Electrical conduit systems
- Underground drainage
- High-pressure water supply
Modern manufacturing has refined PVC compounds to perform better in extreme temperatures, higher pressures, and long-term installations. Some PVC systems installed today are rated to last 50–100 years under proper conditions.
Main Types of PVC Pipes (Explained Simply)
PVC pipes are manufactured in several forms, each designed to perform a specific job efficiently and safely. While they may look similar from the outside, their internal structure, strength, and material composition vary significantly. Choosing the wrong type of PVC pipe can lead to leaks, pressure failure, or long-term damage, even if the pipe appears suitable at first glance.
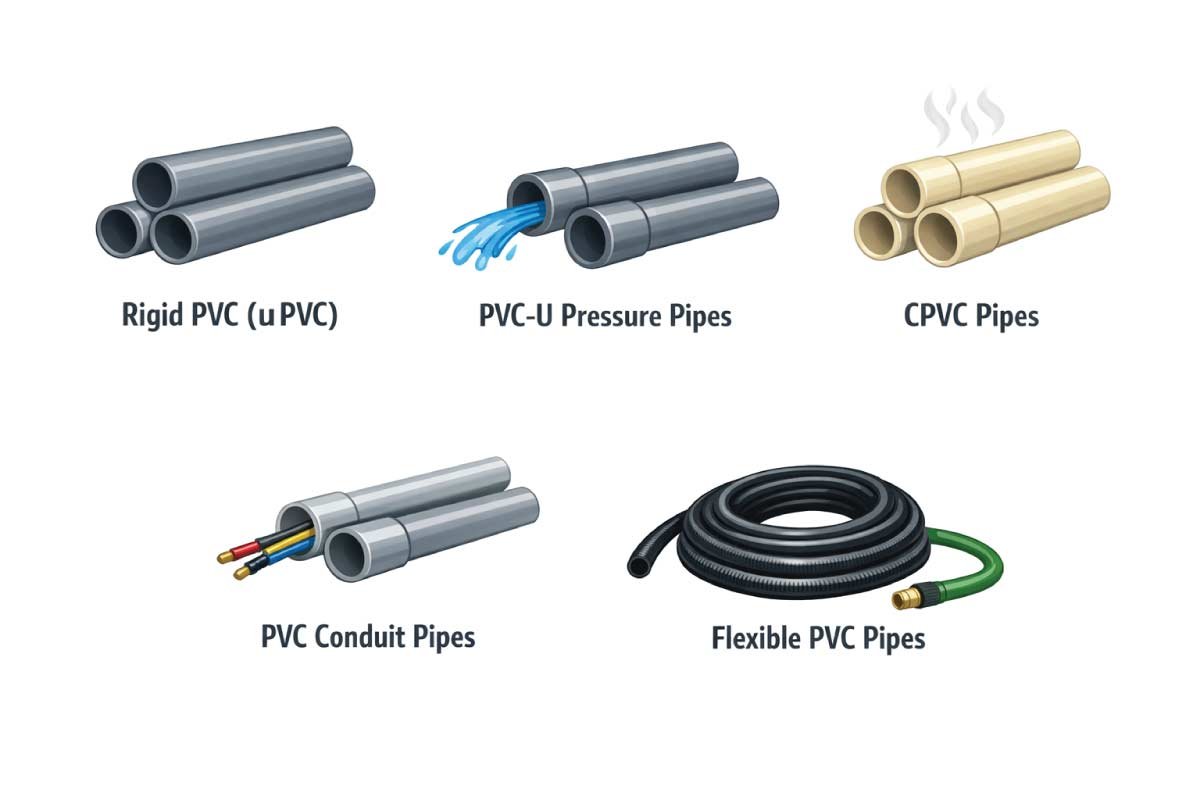

1- Rigid PVC (uPVC)
Rigid PVC, also known as uPVC (unplasticized PVC), is the most widely used PVC pipe type across residential and industrial projects. Because it contains no plasticizers, it remains hard, strong, and dimensionally stable over time. This makes uPVC ideal for permanent installations where strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors are essential.
Common uses include:
Water supply lines
Drainage systems
Sewer pipelines
Irrigation networks
uPVC pipes are highly resistant to chemicals and UV radiation, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations.
2- PVC-U Pressure Pipes
PVC-U pressure pipes are engineered specifically to transport fluids under continuous or variable pressure. They feature thicker walls and precise manufacturing standards that allow them to withstand internal force without deformation. These pipes are commonly used in systems where consistent flow and safety are critical, especially in large-scale or long-distance applications.
You will find them in:
Municipal water systems
Pumped irrigation lines
Industrial fluid transport
Each pipe is marked with a pressure class, ensuring safety and consistency.
3- CPVC Pipes (Chlorinated PVC)
CPVC pipes are produced by adding extra chlorine to standard PVC, which significantly increases their ability to handle higher temperatures. This enhanced heat resistance makes CPVC suitable for hot water supply systems where regular PVC would fail. It also offers improved chemical stability, making it reliable for long-term residential plumbing.
Key advantages:
Handles hot water up to 90–100°C
Better chemical stability
Suitable for residential hot water plumbing
In 2026, CPVC is widely used in modern homes where metal piping is being phased out.
4- PVC Conduit Pipes
PVC conduit pipes are designed to protect electrical wiring rather than transport liquids or gases. Their non-conductive nature provides an added layer of electrical safety, while their smooth interior allows easy cable pulling. These pipes are commonly used in both surface-mounted and concealed electrical installations.
Why they’re preferred:
Fire-resistant
Lightweight
Non-conductive
Easy to install
They are essential in both residential and industrial electrical systems.
5- Flexible PVC Pipes
Flexible PVC pipes contain plasticizers that allow them to bend and curve without cracking, making them useful in areas where rigid pipes cannot be installed easily. They are commonly used for short runs, connections, or temporary setups where movement or vibration is expected. However, they are not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Typical uses:
Swimming pools
Garden hoses
HVAC drainage
Temporary piping setups
They are not designed for high pressure but offer excellent flexibility where rigid piping isn’t practical.
Understanding PVC Pipe Sizes (No More Confusion)
PVC pipe sizing often confuses homeowners and even professionals because it doesn’t follow normal measurement logic. What you see on the label is not always what you measure with a tape. Understanding how PVC sizes actually work helps avoid fitting issues, poor flow performance, and costly installation mistakes—especially in plumbing, irrigation, and industrial systems.

1- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS)
PVC pipe sizes are defined using the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) system, which refers to a standardized name rather than the pipe’s exact physical dimensions. For example, a “2-inch” PVC pipe does not have a 2-inch outside diameter. This naming system allows pipes, fittings, and accessories from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly.
What matters:
Outside Diameter (OD) is standardized
Inside Diameter (ID) varies based on wall thickness
This system ensures compatibility with fittings, valves, and connectors.
2- Schedule System (Schedule 40, 80, and Beyond)
The schedule system describes how thick a PVC pipe’s wall is, not how much pressure it can handle directly. A higher schedule number means a thicker wall and stronger structure. This makes the pipe suitable for more demanding environments, such as higher pressure or industrial use, while keeping the outside diameter consistent.
Schedule 40: Standard residential and light commercial use
Schedule 80: Thicker walls, higher pressure tolerance
Schedule 120: Heavy industrial applications
As the schedule number increases:
Wall thickness increases
Inside diameter decreases
Pressure capacity improves
In 2026, Schedule 40 and Schedule 80 remain the most commonly used worldwide.
3- Common PVC Pipe Diameters
PVC pipes are manufactured in a broad range of diameters to suit everything from small household plumbing to large-scale infrastructure projects. Smaller diameters are typically used for water supply and irrigation, while larger sizes handle higher flow volumes. Choosing the correct diameter ensures proper flow, pressure balance, and long-term system efficiency.
PVC pipes are available in a wide range of sizes, including:
½ inch
¾ inch
1 inch
2 inch
4 inch
6 inch and larger
Large-diameter PVC pipes are frequently used in drainage, sewage, and stormwater systems.
PVC Pipe Materials: What Are They Really Made Of?
PVC pipes are far more than ordinary plastic. Their performance, durability, and suitability for different applications depend heavily on the materials and additives used during manufacturing. Understanding what goes into a pipe helps explain why some PVC pipes can last decades, resist harsh chemicals, and perform reliably under pressure or heat.

1- Core PVC Resin
The core PVC resin forms the backbone of every pipe, giving it strength, chemical resistance, and durability. High-quality resin ensures the pipe maintains structural integrity over years of use, even under heavy flow or extreme weather. It’s this foundation that makes PVC pipes a trusted choice for plumbing, irrigation, and industrial systems.
The base material provides:
Structural strength
Chemical resistance
Longevity
High-quality resin ensures consistent performance over decades.
2- Stabilizers and Additives
Stabilizers and other additives enhance PVC performance, making pipes more resistant to cracking, UV damage, and heat. Modern formulas in 2026 focus on eco-friendly stabilizers that minimize environmental impact while keeping the pipe strong and durable. These enhancements allow PVC to be used outdoors, underground, or in challenging industrial environments safely.
Modern PVC pipes include stabilizers that:
Prevent UV degradation
Reduce brittleness
Improve heat tolerance
In 2026, many manufacturers have shifted to eco-friendly stabilizers, reducing environmental impact without sacrificing durability.
3- Plasticizers (Only in Flexible PVC)
Flexible PVC pipes rely on plasticizers to make the material bendable without cracking. While this increases flexibility, it also reduces pressure tolerance, which is why flexible PVC is not used in high-pressure applications like water mains. The balance between flexibility and strength is crucial to choosing the right pipe for the job.
Plasticizers allow flexibility but reduce pressure capacity. This is why flexible PVC is never used in high-pressure plumbing.
Pressure Ratings and Performance in 2026
Every PVC pipe is carefully tested to determine how much internal pressure it can safely handle. These ratings ensure that pipes perform reliably in homes, industrial systems, and infrastructure projects. Understanding pressure limits helps prevent leaks, bursts, or long-term failures, making proper installation safer and more cost-effective in 2026.
Factors affecting pressure rating:
Pipe diameter
Wall thickness
Temperature
Material formulation
Higher temperatures reduce pressure tolerance, which is why CPVC is preferred for hot water systems. Always check manufacturer markings before installation to ensure the pipe meets your specific pressure and temperature requirements.
Also Read:
Where PVC Pipes Are Used Today
PVC piping is no longer limited to simple home plumbing. Its versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness have made it a key material in modern engineering projects worldwide. From urban infrastructure to residential setups, PVC adapts to a wide range of applications, supporting efficiency, sustainability, and long-term performance in 2026.
In 2026, major applications include:
Smart irrigation systems
Industrial chemical transport
Rainwater harvesting
Renewable energy infrastructure
Modular construction projects
Its adaptability, combined with low maintenance and long lifespan, makes PVC a core material across residential, industrial, and environmental projects.
Also Read:
Advantages of PVC Pipes Over Metal Pipes
PVC continues to replace metal piping in homes, industries, and infrastructure due to its unmatched combination of durability, cost-efficiency, and ease of use. Unlike metal, PVC resists corrosion and scaling, making it ideal for long-term applications. Its smooth surface ensures efficient flow, while lightweight construction simplifies handling and installation, reducing labor and material costs over time.
Key benefits:
No corrosion or rust
Lightweight and easy to install
Lower cost
Smooth internal surface (better flow)
Minimal maintenance
These advantages translate into lower lifetime costs and fewer failures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PVC pipes have sometimes been criticized for environmental reasons, but advances in manufacturing and recycling have significantly improved their sustainability profile. Modern PVC pipes are designed for long service life, reducing material waste, and many now use eco-friendly additives. Proper installation ensures efficiency, making PVC a responsible choice in 2026 for environmentally conscious projects.
In 2026:
PVC pipes are recyclable
Production emissions have decreased
Longer service life reduces replacement waste
When installed correctly, PVC piping is one of the most resource-efficient solutions available.
Also Read:
Choosing the Right PVC Pipe (Practical Advice)
Selecting the right PVC pipe requires a careful look at the project’s requirements. The correct pipe type, size, and material ensure system longevity, safety, and efficiency. Factors like pressure, temperature, and local building codes should always guide your choice. A well-informed selection upfront prevents leaks, failures, and costly replacements in the long run.
Before selecting a PVC pipe, always consider:
Application type (water, drainage, electrical)
Pressure requirements
Temperature exposure
Local building codes
Choosing correctly at the start prevents costly repairs later.
Final Thoughts: Why PVC Pipes Still Matter
PVC pipes may not be glamorous, but they are foundational to modern life. Clean water, safe drainage, reliable power, and efficient infrastructure all depend on choosing the right materials.
Understanding PVC pipe types, sizes, and materials empowers you to make informed decisions—whether you’re fixing a small leak or planning a large-scale project.
In 2026 and beyond, PVC remains not just relevant, but essential.
Also Read:
FAQs About PVC Pipes
What is PVC pipe and why is it so popular?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a lightweight, durable plastic pipe known for resisting corrosion, rust, and chemical reactions. Its low cost, smooth interior for better flow, and long lifespan make it ideal for residential plumbing, industrial systems, and irrigation. In 2026, PVC remains popular due to its adaptability and reliability in multiple applications.
What are the main types of PVC pipes?
PVC pipes come in several types, including rigid PVC (uPVC), PVC-U pressure pipes, CPVC for hot water, conduit pipes for electrical wiring, and flexible PVC. Each type is designed for specific uses, from water supply to industrial chemical transport. Choosing the correct type ensures long-term performance and prevents leaks or failures.
How are PVC pipe sizes measured?
PVC pipes use the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) system, which doesn’t always match the actual outside diameter. Wall thickness is described by the Schedule system, such as Schedule 40 or 80. Correct sizing ensures compatibility with fittings and proper flow. Understanding these measurements prevents installation errors and long-term issues in plumbing or irrigation projects.
What materials are used in PVC pipes?
PVC pipes are made from high-quality PVC resin for strength and chemical resistance, stabilizers to reduce brittleness and UV damage, and plasticizers in flexible pipes for bendability. Modern formulations in 2026 often include eco-friendly additives, improving sustainability while maintaining long-term durability and performance across residential, industrial, and outdoor applications.
What affects PVC pipe pressure ratings?
Pressure ratings depend on pipe diameter, wall thickness, temperature, and material formulation. Higher temperatures reduce pressure tolerance, which is why CPVC is preferred for hot water. Always checking manufacturer markings ensures the pipe is suitable for its intended application, preventing leaks, bursts, and failures in plumbing, irrigation, or industrial systems.
Where are PVC pipes commonly used today?
PVC pipes are used in residential plumbing, industrial chemical transport, smart irrigation, rainwater harvesting, renewable energy systems, and modular construction. Their versatility, low maintenance, and long lifespan make them ideal for modern engineering projects. In 2026, PVC piping continues to be a core material in both domestic and industrial applications worldwide.
7. Why choose PVC pipes over metal pipes?
PVC pipes are corrosion-resistant, lightweight, easier to install, and cost-effective. Their smooth interior ensures better flow, and minimal maintenance reduces long-term costs. Modern PVC pipes are recyclable, eco-friendly, and durable, making them more sustainable than metal pipes. These advantages explain why PVC remains the preferred choice for plumbing and industrial projects in 2026.

