When working with pipes—whether in home plumbing, industrial systems, or mechanical setups—tee fittings are among the most commonly used components. A small mistake in tee fitting size selection can lead to leaks, pressure loss, or even system failure. That’s why understanding a tee fitting size chart is essential before starting any project.
In this detailed guide, we will break down tee fitting sizes, explain how they are measured, and provide easy-to-read charts for different materials and standards. By the end, you will know exactly how to choose the right tee fitting for your application with confidence.
What Is a Tee Fitting?
Tee fittings typically have three openings:
- One inlet
- Two outlets (or vice versa)
They are widely used in:
- Residential plumbing
- HVAC systems
- Industrial piping
- Automotive and mechanical assemblies
- Irrigation systems
Why Tee Fitting Size Matters
Selecting the correct tee fitting size is critical for the safety, efficiency, and long-term performance of any piping system. Even a small sizing mismatch can create serious operational problems, increase maintenance costs, and reduce system reliability, especially in plumbing, mechanical, and industrial installations.
Choosing the wrong tee fitting size can cause:
Leakage due to poor sealing
Reduced flow rate
Pressure imbalance
Premature wear of pipes and joints
Pipe systems rely on precise inner and outer diameters, so tee fittings must match the pipe size exactly—not approximately.
Types of Tee Fittings by Configuration
Tee fittings are available in different configurations to suit specific piping needs, flow requirements, and installation methods. Each type is designed to handle pressure, material compatibility, and connection style differently. Understanding these tee fitting configurations helps you select the right fitting for efficient flow distribution, system durability, and long-term reliability.

1. Equal Tee
An equal tee has three openings of the same size, allowing fluid or gas to flow evenly in multiple directions. It is commonly used in plumbing, HVAC, and industrial piping systems where uniform pipe diameter is required. Equal tees ensure balanced pressure distribution and are ideal for symmetrical pipeline layouts.
2. Reducing Tee
A reducing tee features one branch that is smaller than the main run, allowing a controlled reduction in flow size. This type is often used when connecting a smaller pipe to a larger main line. Reducing tees help manage pressure changes and are widely used in water supply, gas lines, and industrial distribution systems.
3. Barbed Tee
A barbed tee is designed for flexible tubing and hoses, with ridged ends that grip the hose securely. It is commonly used in irrigation systems, fuel lines, pneumatic setups, and low-pressure fluid applications. Barbed tees are easy to install and typically require hose clamps to ensure a leak-free connection.
4. Threaded Tee
A threaded tee includes internal or external threads that allow it to screw directly onto threaded pipes. This type is preferred where frequent disassembly, maintenance, or system modification is required. Threaded tees are widely used in plumbing, air systems, and mechanical installations, especially where welding is not practical.
5. Welded / Socket Tee
A welded or socket tee is designed for permanent installations where strength and leak resistance are critical. These fittings are commonly welded or solvent-welded to the pipe, creating a strong, sealed joint. They are widely used in high-pressure industrial systems, chemical pipelines, and long-term infrastructure projects.
Standard Tee Fitting Size Chart (Nominal Pipe Size)
This chart provides the standard sizes for steel, galvanized, and iron pipes using NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) standards. It helps ensure proper selection of tee fittings for accurate pipe connections and reliable system performance.
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Outside Diameter (OD) | Inside Diameter (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | 0.840 in (21.34 mm) | 0.622 in (15.8 mm) |
| 3/4 inch | 1.050 in (26.67 mm) | 0.824 in (20.9 mm) |
| 1 inch | 1.315 in (33.40 mm) | 1.049 in (26.6 mm) |
| 1 1/4 inch | 1.660 in (42.16 mm) | 1.380 in (35.1 mm) |
| 1 1/2 inch | 1.900 in (48.26 mm) | 1.610 in (40.9 mm) |
| 2 inch | 2.375 in (60.33 mm) | 2.067 in (52.5 mm) |
PVC Tee Fitting Size Chart (Schedule 40)
PVC tee fittings are measured primarily by outside diameter (OD) and are widely used in residential, commercial, and irrigation systems. This chart helps you select the correct PVC tee for proper pipe connections, ensuring leak-free installation, efficient flow, and long-lasting performance in lightweight, corrosion-resistant applications.
| PVC Pipe Size | Outside Diameter (OD) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | 0.840 in (21.34 mm) | Household plumbing |
| 3/4 inch | 1.050 in (26.67 mm) | Water supply lines |
| 1 inch | 1.315 in (33.40 mm) | Irrigation systems |
| 1 1/2 inch | 1.900 in (48.26 mm) | Drainage systems |
| 2 inch | 2.375 in (60.33 mm) | Waste & vent pipes |
| 3 inch | 3.500 in (88.90 mm) | Sewer lines |
✔ PVC tees are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to install.
Threaded Tee Fitting Size Chart (NPT)
Threaded tee fittings feature internal or external threads, allowing easy assembly and disassembly of piping systems. This chart provides standard NPT sizes, threads per inch, and typical uses, making it easier to select the right threaded tee for plumbing, industrial, and mechanical applications while maintaining leak-free performance.
| Thread Size (NPT) | Threads per Inch (TPI) | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| 1/8 inch | 27 | Instrument lines |
| 1/4 inch | 18 | Air fittings |
| 3/8 inch | 18 | Fuel systems |
| 1/2 inch | 14 | Plumbing |
| 3/4 inch | 14 | Industrial piping |
| 1 inch | 11.5 | High-flow systems |
⚠ Always use thread seal tape or pipe dope for leak-free joints.
Metric Tee Fitting Size Chart
Metric tee fittings are commonly used in automotive, pneumatic, and international piping systems. This chart shows pipe outer diameters and their inch equivalents, simplifying the selection process for metric pipelines and ensuring proper flow distribution and compatibility across various applications.
| Pipe Outer Diameter (mm) | Equivalent Inch Size |
|---|---|
| 10 mm | ~3/8 inch |
| 12 mm | ~1/2 inch |
| 16 mm | ~5/8 inch |
| 20 mm | ~3/4 inch |
| 25 mm | ~1 inch |
| 32 mm | ~1 1/4 inch |
Reducing Tee Size Chart (Example)
Reducing tees allow a branch line to be smaller than the main run, enabling efficient flow management and pressure control. This chart highlights common reducing tee sizes, helping you design water, gas, and multi-line distribution systems with accurate connections and long-term reliability.
| Main Run Size | Branch Size |
|---|---|
| 1 inch | 1/2 inch |
| 1 1/2 inch | 3/4 inch |
| 2 inch | 1 inch |
| 3 inch | 2 inch |
| 4 inch | 2 inch |
These are widely used in:
- Pressure regulation
- Multi-line distribution systems
- Water and gas supply networks
Also Read:
Materials Commonly Used in Tee Fittings
Tee fittings are made from different materials, each affecting durability, sizing tolerances, and system performance. Choosing the correct material ensures reliability under pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions, whether in residential plumbing, industrial pipelines, or mechanical systems.
1- Metal Tee Fittings
Metal tee fittings, such as steel, stainless steel, brass, and copper, are ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They provide excellent strength, durability, and long-term performance in mechanical, industrial, and plumbing systems.
✔ High strength
✔ Suitable for pressure and heat
2- Plastic Tee Fittings
Plastic tee fittings—including PVC, CPVC, PEX, and HDPE are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to install. They are perfect for water supply, drainage, and chemical applications where metal fittings are unnecessary or cost-prohibitive.
✔ Corrosion-resistant
✔ Lightweight and cost-effective
Also Read:
How to Choose the Right Tee Fitting Size
Selecting the correct tee fitting size is essential for a safe, efficient, and long-lasting piping system. Proper sizing ensures optimal flow, prevents leaks, reduces maintenance, and avoids pressure issues. Following a structured approach helps you choose the right tee for your specific material, pressure, and application requirements.
Follow these simple steps:
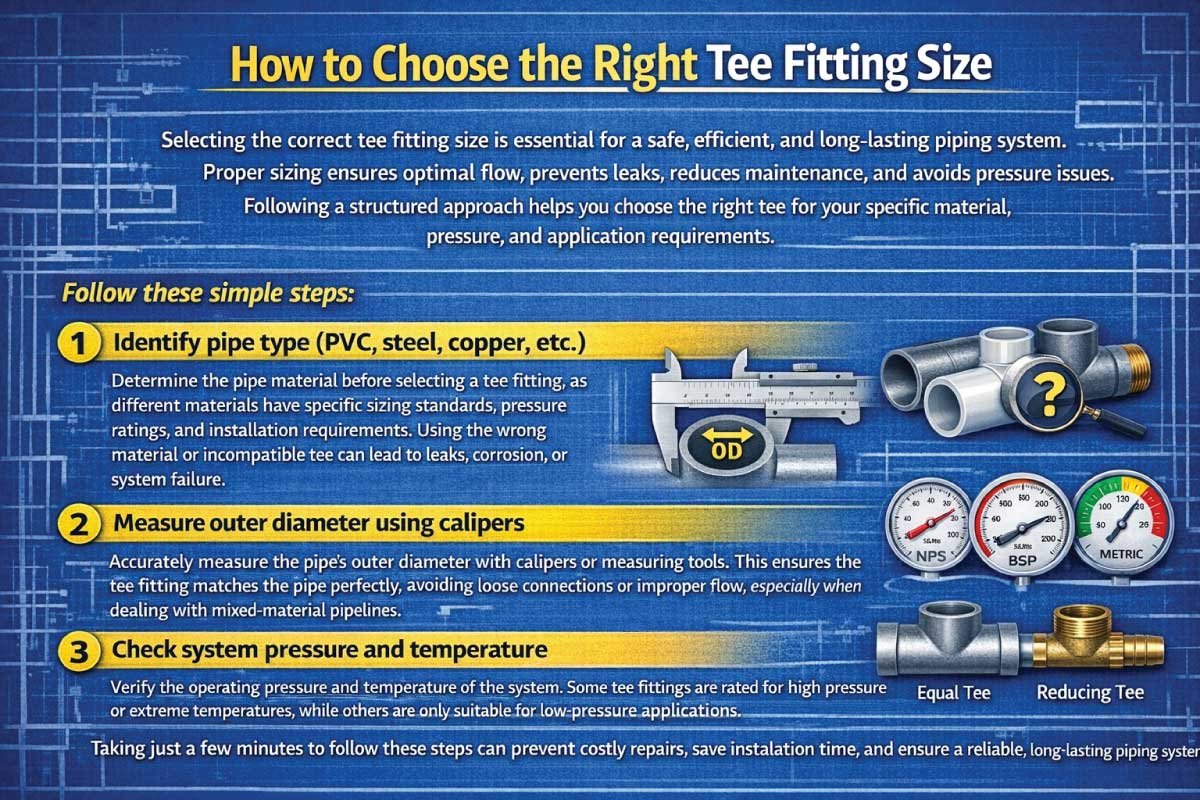
1- Identify pipe type (PVC, steel, copper, etc.)
Determine the pipe material before selecting a tee fitting, as different materials have specific sizing standards, pressure ratings, and installation requirements. Using the wrong material or incompatible tee can lead to leaks, corrosion, or system failure.
2- Measure outer diameter using calipers
Accurately measure the pipe’s outer diameter with calipers or measuring tools. This ensures the tee fitting matches the pipe perfectly, avoiding loose connections or improper flow, especially when dealing with mixed-material pipelines.
3- Check system pressure and temperature
Verify the operating pressure and temperature of the system. Some tee fittings are rated for high pressure or extreme temperatures, while others are only suitable for low-pressure applications. Correct ratings prevent damage and ensure safety.
4- Match the fitting standard (NPS, BSP, NPT, Metric)
Tee fittings come in various standards like NPS, BSP, NPT, or Metric. Ensure the fitting standard aligns with your pipe to maintain proper threading, size compatibility, and leak-free connections.
5- Confirm equal or reducing tee requirement
Decide whether you need an equal tee or a reducing tee based on flow requirements. Equal tees maintain uniform pipe size, while reducing tees allow smaller branch lines, helping control pressure and flow distribution.
Taking just a few minutes to follow these steps can prevent costly repairs, save installation time, and ensure a reliable, long-lasting piping system.
Also Read:
Common Tee Fitting Size Mistakes to Avoid
Even small errors when selecting or installing tee fittings can lead to leaks, system failures, or reduced performance. Understanding common mistakes helps prevent costly repairs and ensures long-term reliability. By being aware of these pitfalls, both beginners and experienced installers can maintain safe, efficient, and properly functioning piping systems.
- Assuming inch size equals actual diameter
- Mixing metric and imperial fittings
- Using threaded tees on non-threaded pipes
- Ignoring pressure ratings
- Over-tightening threaded tees
These mistakes are common even among experienced installers.
Also Read:
Applications of Tee Fittings by Size
ee fittings are used in a wide range of plumbing, mechanical, and industrial systems. Selecting the correct size ensures proper flow, pressure distribution, and system efficiency. This chart highlights typical applications for each tee fitting size, helping you choose the right fitting for your specific project.
| Tee Size | Typical Application |
|---|---|
| 1/2 inch | Home plumbing, RO systems |
| 3/4 inch | HVAC, water supply |
| 1 inch | Irrigation, pumps |
| 2 inch | Drainage systems |
| 3 inch+ | Industrial pipelines |
Final Thoughts
A tee fitting size chart is more than just a table—it’s a roadmap to safe, efficient, and long-lasting pipe installations. Whether you’re working on a small DIY plumbing task or managing a large industrial system, choosing the correct tee fitting size ensures smooth flow, strong connections, and peace of mind.
Always double-check pipe standards, measure accurately, and refer to trusted size charts before installation. A properly sized tee fitting may be small, but its impact on system performance is huge.
Also Read:
Wheel Lug Nut Size Chart (2026): Complete Guide
FAQs:
What is the standard tee size?
The standard tee size depends on the pipe system and material. For steel, iron, or galvanized pipes, it follows NPS (Nominal Pipe Size) standards, while PVC uses outside diameter (OD). Standard tees are available in sizes from 1/2 inch up to 4 inches or more, depending on the application and flow requirements.
How to measure a tee fitting?
To measure a tee fitting, first identify the pipe type. Use calipers to measure the outside diameter (OD) for plastic pipes or refer to NPS standards for metal pipes. For threaded tees, also check the thread size (NPT or BSP). Accurate measurements ensure proper fitting, leak-free connections, and efficient system performance.
How to write tee size?
Tee sizes are typically written using the format: main run size × branch size. For example, a 2×1/2 inch tee indicates the main pipe is 2 inches while the branch is 1/2 inch. Equal tees are simply written as the same size on all three openings, e.g., 1 inch × 1 inch × 1 inch.
How to calculate fitting size?
Fitting size is calculated by considering the pipe type, outer diameter, and required flow. For reducing tees, determine the main run size and branch size. For threaded or NPT fittings, use the nominal pipe size and thread pitch. Correct calculations prevent leaks, pressure loss, and ensure proper flow distribution in the system.
How to choose tee size?
To choose the right tee size, first identify the pipe material and diameter. Check the system’s pressure and temperature ratings. Decide if you need an equal or reducing tee, and ensure the fitting standard matches your pipes (NPS, BSP, NPT, Metric). Proper sizing ensures safe, efficient, and long-lasting piping connections.
What is a standard tee?
A standard tee is a pipe fitting with three openings, typically equal in size, designed to distribute or combine flow in a piping system. It is widely used in plumbing, HVAC, and industrial systems. Standard tees follow pipe sizing standards such as NPS, OD, or metric, depending on the material and application.
How to size NPT fittings?
NPT (National Pipe Thread) fittings are sized using the nominal pipe size (NPS) and threads per inch (TPI). Identify the pipe’s NPS, then match the corresponding NPT fitting with the correct internal or external threads. Proper sizing ensures leak-free connections, easy assembly, and compatibility with standard piping systems.


