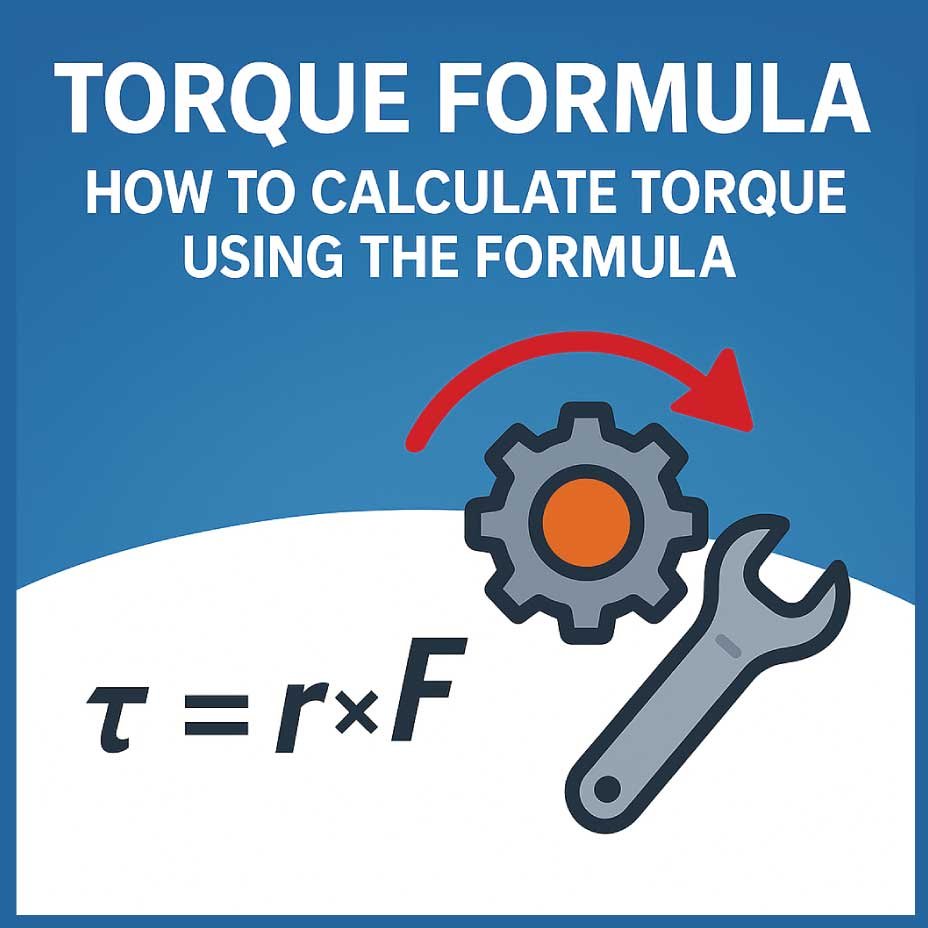
Torque is calculated using the following standard formula:
τ = F × r × sin(θ)
Where:
τ (tau) is the torque
F is the applied force
r is the distance (lever arm) from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied
θ is the angle between the force vector and the lever arm
In the most common cases where the force is applied perpendicularly to the lever arm, the angle θ is 90°, and the formula simplifies to:
τ = F × r
This simplified formula is widely used in engineering when the force direction is at a right angle to the lever arm.
How to Calculate Torque Using the Formula
To calculate torque, you need three main components:
Force (F) – The amount of force applied (in Newtons, N)
Distance (r) – The perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied (in meters, m)
Angle (θ) – The angle between the direction of the force and the lever arm (in degrees or radians)
The general formula is:
Torque (τ) = F × r × sin(θ)
Step-by-Step Calculation:
Identify the force (F):
For example, 50 N of force applied.Measure the lever arm (r):
Suppose the force is applied 0.3 meters from the rotation axis.Determine the angle (θ):
If the force is applied at a 90° angle, then sin(90°) = 1.Apply the formula:
τ = 50 N × 0.3 m × sin(90°)
τ = 50 × 0.3 × 1 = 15 Nm
Result:
Torque = 15 Newton-meters (Nm)
Also Read: