Manufacturing is the backbone of modern industry, shaping the products we use every day, from the smartphones in our hands to the cars on the streets. Understanding how manufacturing works can seem complicated, but it becomes much easier when broken down into simple steps. In this guide, we’ll explore 7 easy steps to understand manufacturing, giving you a clear picture of the entire process in just a few minutes.
Step 1: Idea and Design
Every manufacturing process starts with an idea. Before anything is produced, someone must think about what product is needed and how it should look, function, and perform. This step involves brainstorming, researching the market, and identifying the customer’s needs.
Once the idea is solid, it moves into the design phase. Engineers and designers create detailed plans, drawings, or digital 3D models that outline the product’s dimensions, features, and materials. This blueprint ensures that everyone involved in production knows exactly what to make.
Key point: A clear design reduces errors later and makes the production process smoother.
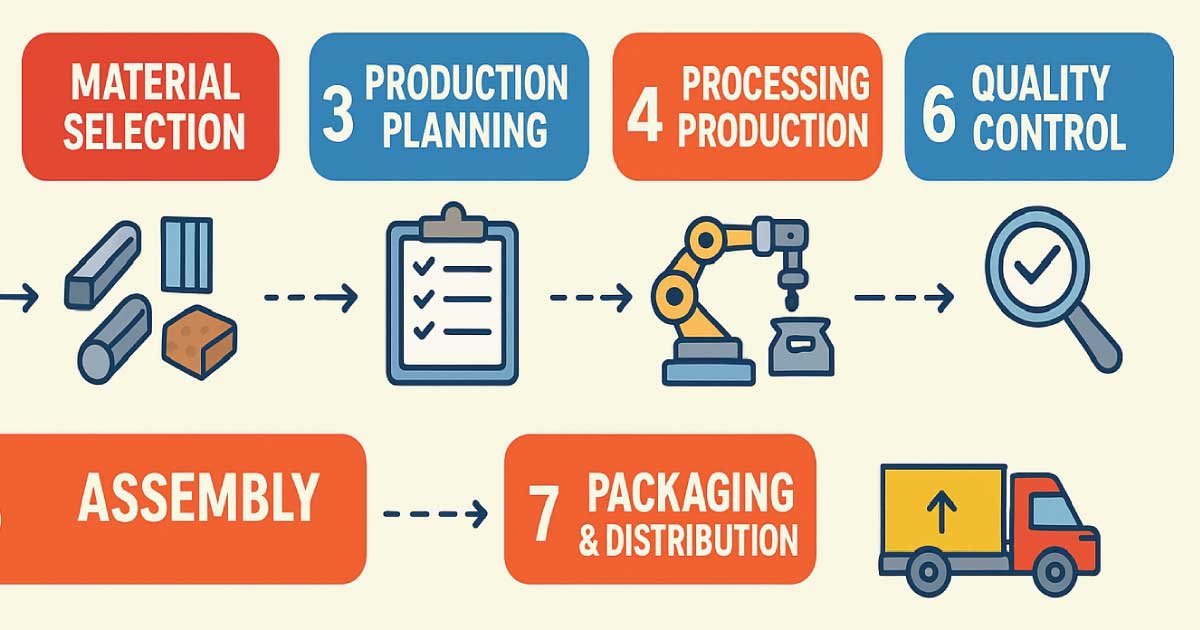
Step 2: Material Selection
After finalizing the design, the next step is to choose the right materials. Materials can range from metals, plastics, and wood to textiles and chemicals, depending on the product. The selection is crucial because it affects the product’s strength, durability, appearance, and cost.
Manufacturers often consider factors such as availability, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. For example, an eco-friendly product may use recycled plastics or sustainably sourced wood.
Key point: Choosing the correct materials ensures quality and longevity of the product.
Step 3: Production Planning
Before any physical production begins, manufacturers create a production plan. This plan outlines the sequence of steps required to make the product, including the machines, tools, and human resources needed.
Planning also involves estimating timelines and costs to ensure the process is efficient. A well-thought-out production plan can save time, reduce waste, and prevent costly mistakes.
Key point: Planning streamlines the manufacturing process and ensures resources are used efficiently.
Step 4: Processing/Production
This is where the real transformation happens. Raw materials are processed into components or parts of the product. Depending on the industry, this step may involve:
Machining: Cutting, drilling, or shaping materials using machines.
Molding: Forming materials like plastic or metal into specific shapes.
Fabrication: Assembling components into sub-parts or frames.
At this stage, precision is critical. Advanced machinery and automated systems help maintain accuracy, while skilled workers oversee operations to handle tasks that require human judgment.
Key point: The production stage turns raw materials into usable components, forming the foundation of the final product.
Step 5: Assembly
Once all components are ready, they are assembled to create the final product. Assembly can be manual, automated, or a combination of both. For example, in car manufacturing, robots handle heavy welding tasks, while humans install smaller interior parts.
Efficiency and accuracy are essential during assembly. Even a small error in fitting parts can lead to product failure, so quality checks often begin during this stage.
Key point: Proper assembly ensures that the product functions correctly and meets design specifications.
Step 6: Quality Control
Quality control (QC) is an essential step in manufacturing. Even if a product is designed well, uses the best materials, and is assembled carefully, it still needs thorough inspection to ensure it meets standards.
What happens in quality control?
Visual Inspections: Products are checked for visible defects such as scratches, dents, or misalignments.
Functional Tests: Components and the final product are tested to ensure they operate correctly. For example, electronic devices undergo power-on tests, while machinery is checked for smooth movement.
Dimensional Checks: Using precise instruments, manufacturers verify that components meet exact measurements.
Quality control prevents defective products from reaching customers, protecting the brand’s reputation and reducing returns or complaints. Modern manufacturing often uses automated systems like sensors and cameras, but skilled workers are still vital for detailed inspection.
Key point: QC ensures that every product leaving the factory is reliable, safe, and meets design expectations.
Step 7: Packaging and Distribution
The final step in manufacturing is packaging and distribution. Even a perfect product can be damaged or lost if it isn’t packaged properly. Packaging protects the product, makes it easier to handle, and provides important information to consumers, like instructions or safety warnings.
Packaging types:
Protective Packaging: Foam, bubble wrap, or molded trays prevent physical damage during transport.
Retail Packaging: Attractive boxes or labels designed to appeal to customers.
Bulk Packaging: Larger containers used for shipping multiple units efficiently.
After packaging, the products are ready for distribution. Manufacturers use logistics systems to deliver products to warehouses, retailers, or directly to customers. Efficient distribution ensures products arrive on time, in good condition, and at a reasonable cost.
Key point: Proper packaging and smart distribution are critical for customer satisfaction and business success.
Why Understanding Manufacturing Matters
Understanding manufacturing is valuable for several reasons:
Improved Decision-Making: Knowing how products are made helps businesses choose the right materials, suppliers, and production methods.
Better Product Design: Awareness of manufacturing constraints leads to designs that are easier and more cost-effective to produce.
Career Opportunities: Manufacturing knowledge opens doors to careers in engineering, production management, quality control, and logistics.
Consumer Awareness: Even as a consumer, understanding manufacturing helps you make informed choices about product quality and sustainability.
Summary of the 7 Steps
To recap, here’s a quick overview of the 7 easy steps of manufacturing:
Idea & Design: Brainstorm, research, and create detailed plans.
Material Selection: Choose the right raw materials for durability, cost, and sustainability.
Production Planning: Organize resources, timelines, and processes efficiently.
Processing/Production: Transform raw materials into components using machines and skilled labor.
Assembly: Put all components together to form the final product.
Quality Control: Inspect, test, and verify that products meet high standards.
Packaging & Distribution: Protect the product and deliver it to customers safely.
Each step is interconnected, and skipping or neglecting one can affect the final product’s quality, cost, and timeliness. Understanding these steps gives you a clear picture of how the items we use every day go from an idea in a designer’s mind to a product in your hands.
Conclusion
Manufacturing doesn’t have to be complicated. By breaking it down into 7 easy steps, anyone can grasp how products are created, tested, and delivered. From the initial concept to the finished product, each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring quality, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Next time you use a product, take a moment to think about the journey it went through – the idea, materials, assembly, checks, and careful delivery – all happening behind the scenes in the fascinating world of manufacturing.
Also Read: