When it comes to vehicle safety, few components are as small yet as critical as wheel lug nuts. They are responsible for keeping your wheels securely attached to the vehicle, handling road stress, and ensuring proper alignment. Choosing the correct lug nut size is not just a technical detail—it’s a matter of safety, performance, and peace of mind.
This complete guide will walk you through wheel lug nut sizes, thread types, seat styles, torque values, and provide easy-to-read size charts for popular vehicles. Whether you’re replacing lug nuts, installing aftermarket wheels, or just checking compatibility, this guide will help you do it right.
What Is a Wheel Lug Nut?
- Proper wheel alignment
- Even load distribution
- Secure braking and steering
- Safe high-speed driving
Using the wrong size or type can cause stripped threads, loose wheels, vibration, or even wheel detachment.
Why Lug Nut Size Matters
- Thread size
- Thread pitch
- Seat type
- Length
- Material
Even a small mismatch can lead to serious mechanical issues.
Problems Caused by Incorrect Lug Nuts
Using the wrong lug nuts can lead to several serious issues:
Cross-threading wheel studs – damaging threads and making installation difficult.
Uneven wheel seating – causing imbalance and vibrations.
Brake rotor damage – from improper pressure distribution.
Wheel wobble or vibration – affecting handling and safety.
Stud breakage over time – risking wheel detachment and accidents.
Understand Lug Nut Size Terminology
Before choosing or replacing lug nuts, it’s essential to understand the terminology. Knowing the differences in thread size, thread pitch, and seat type helps ensure proper fitment, prevents damage to studs or wheels, and guarantees safe driving. Familiarity with these terms makes selecting the right lug nuts much easier.
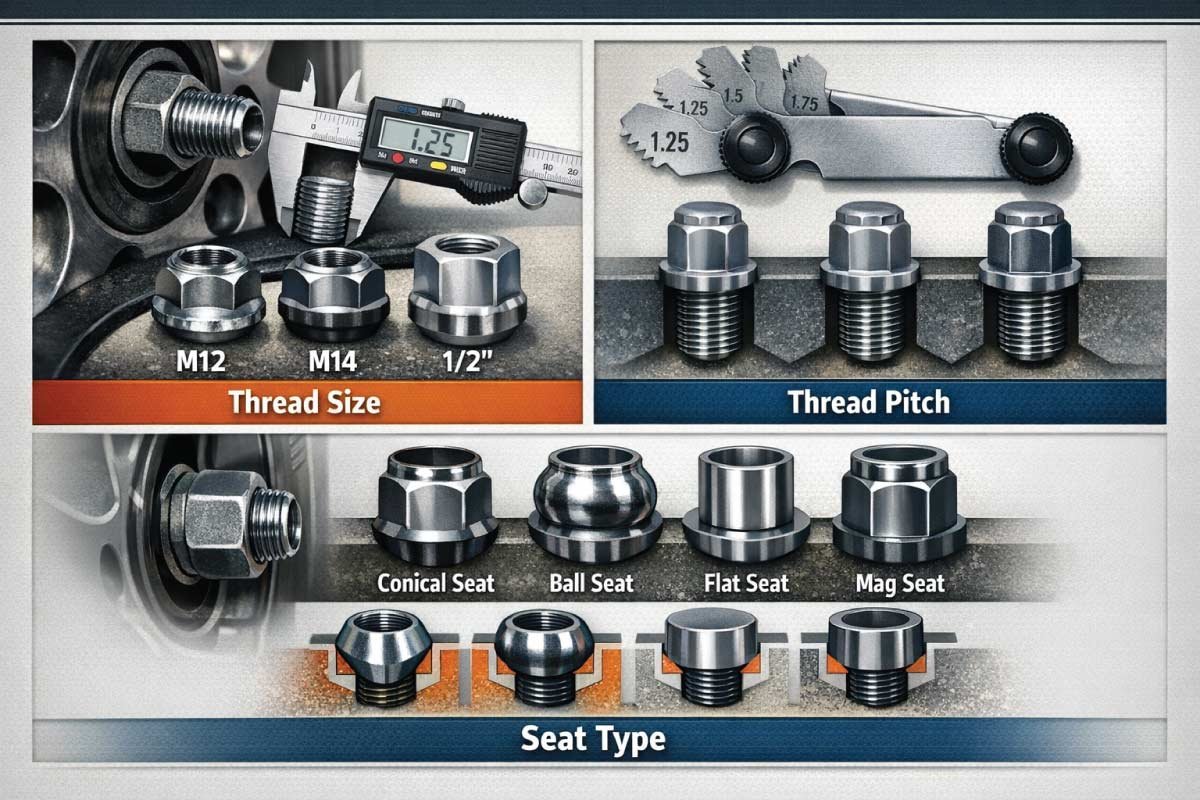
1. Thread Size
Thread size refers to the diameter of the wheel stud the lug nut fits onto. Common sizes include M12, M14, and 1/2 inch for U.S. vehicles. Choosing the correct thread size ensures the lug nut fits securely, avoids cross-threading, and maintains proper wheel alignment for safe, reliable driving.
2. Thread Pitch
Thread pitch is the distance between threads on a lug nut or stud. Examples include M12x1.25, M12x1.5, and M14x1.5. Selecting the correct pitch prevents stripped threads, ensures proper torque application, and keeps wheels securely attached, which is critical for both vehicle safety and optimal wheel performance.
3. Seat Type
Seat type describes the part of the lug nut that contacts the wheel. Common types include conical (acorn), ball (radius), flat, and mag seats. Matching the seat type to your wheel ensures proper seating, prevents vibrations, protects the wheel finish, and maintains even load distribution for safe driving.
| Seat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Conical (Acorn) | Tapered 60° seat (most common) |
| Ball (Radius) | Rounded seat (common on European cars) |
| Flat | Flat washer-style seat |
| Mag | Flat seat with extended shank |
Standard Wheel Lug Nut Size Chart (Metric)
Metric lug nuts are the most common type used in modern vehicles worldwide. They vary in thread size and pitch depending on the manufacturer and model. Using the correct metric lug nut ensures proper wheel fitment, prevents damage to studs, and maintains safety and stability while driving.
| Thread Size | Thread Pitch | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| M12 | 1.25 | Toyota, Honda, Subaru |
| M12 | 1.5 | Ford, Chevrolet, Nissan |
| M14 | 1.5 | BMW, Audi, VW |
| M14 | 1.25 | Mercedes-Benz |
| M10 | 1.25 | Compact vehicles |
Standard Wheel Lug Nut Size Chart (SAE / Inch)
Metric lug nuts are the most common type used in modern vehicles worldwide. They vary in thread size and pitch depending on the manufacturer and model. Using the correct metric lug nut ensures proper wheel fitment, prevents damage to studs, and maintains safety and stability while driving.
| Thread Size | Thread Pitch | Common Vehicles |
|---|---|---|
| 1/2″-20 | 20 TPI | Ford, Chevy, Dodge |
| 7/16″-20 | 20 TPI | Older compact cars |
| 9/16″-18 | 18 TPI | Heavy-duty trucks |
Vehicle-Specific Lug Nut Size Chart
Different vehicles use specific lug nut sizes, thread pitches, and seat types. Knowing your vehicle’s exact lug nut specifications is essential when replacing or upgrading wheels. Using the correct lug nuts ensures proper wheel seating, avoids damage, and maintains safe driving performance across all road conditions.
Common Car Brands Lug Nut Sizes
| Vehicle Brand | Lug Nut Size | Thread Pitch | Seat Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toyota | M12x1.5 | 1.5 | Conical |
| Honda | M12x1.5 | 1.5 | Conical |
| Nissan | M12x1.25 | 1.25 | Conical |
| Ford | 1/2″-20 | 20 TPI | Conical |
| Chevrolet | 1/2″-20 | 20 TPI | Conical |
| BMW | M14x1.25 | 1.25 | Ball |
| Mercedes | M14x1.5 | 1.5 | Ball |
| Audi | M14x1.5 | 1.5 | Ball |
| Subaru | M12x1.25 | 1.25 | Conical |
⚠️ Always verify with your owner’s manual, as trims and model years can vary.
Lug Nut Torque Specifications Chart
Proper torque is crucial to ensure lug nuts hold the wheel securely without damaging studs or rotors. Over-tightening can stretch or break studs, while under-tightening can cause loose wheels and unsafe driving conditions. Always follow manufacturer torque specifications for safety, wheel longevity, and optimal performance.
| Vehicle Type | Torque Range (ft-lb) |
|---|---|
| Compact Cars | 80–100 |
| Sedans | 90–110 |
| SUVs | 100–130 |
| Light Trucks | 120–150 |
| Heavy Trucks | 140–160 |
Using too much torque can stretch studs, while too little can cause wheels to loosen.
Also Read:
Types of Lug Nuts Explained
Lug nuts come in different shapes and designs to fit various wheel types and vehicles. Choosing the correct type ensures proper seating, prevents wheel damage, and maintains safety. Each type has unique features, benefits, and applications, from common vehicles to specialty and aftermarket wheels.

1. Acorn (Conical Seat)
Acorn lug nuts are the most common type found on modern vehicles. They feature a 60-degree tapered seat that ensures the wheel seats properly on the hub. Easy to find and replace, conical seat lug nuts are ideal for most factory wheels and provide reliable torque retention, making them a safe, everyday choice.
2. Ball Seat
Ball seat lug nuts are primarily used on European vehicles such as BMW, Mercedes, and Audi. They have a rounded contact surface that matches the wheel seat precisely. Using the wrong seat type can cause wheel wobble or uneven pressure, so it’s important to match ball seat lug nuts to the factory wheel design for proper safety.
3. Mag Seat
Mag seat lug nuts feature a flat washer-style seat and are commonly found on aftermarket or custom wheels. Their flat design helps distribute torque evenly across the wheel surface. While not as common on factory wheels, mag seat lug nuts are versatile for performance or style-oriented setups and provide secure, reliable fastening.
4. Spline Drive
Spline drive lug nuts require a special key to install or remove, offering added theft protection for aftermarket wheels. Their unique ridged design grips the wheel stud securely, preventing loosening under high torque. Spline drive lug nuts are popular with car enthusiasts who want both security and performance for custom or expensive wheels.
5. Extended Lug Nuts
Extended lug nuts are longer than standard nuts, often used with aftermarket wheels that sit further from the hub. They ensure full thread engagement for safety while allowing proper clearance for custom wheels or brake calipers. Correct sizing is crucial, as too short or too long nuts can compromise torque and wheel security.
6. Locking Lug Nuts
Locking lug nuts include a unique pattern or key that prevents unauthorized removal. They are commonly used on aftermarket or high-value wheels to prevent theft. Locking nuts must be installed carefully with the matching key and properly torqued. Using them ensures security without sacrificing wheel fitment or driving safety.
Also Read:
Factory vs Aftermarket Wheels: Lug Nut Differences
When upgrading or replacing wheels, lug nut compatibility is crucial for safety and performance. Factory lug nuts are designed specifically for the vehicle and its original wheels, while aftermarket wheels may require different seat types, lengths, or styles. Using the wrong lug nuts can cause wheel damage, vibrations, or unsafe driving conditions.
| Feature | Factory Wheels | Aftermarket Wheels |
|---|---|---|
| Seat Type | Fixed | Varies |
| Lug Nut Length | Standard | Often longer |
| Locking Option | Rare | Common |
| Torque Sensitivity | Medium | High |
Never reuse factory lug nuts on aftermarket wheels unless the seat type matches exactly.
How to Measure Your Lug Nut Size at Home
Measuring your lug nut size at home is simple and essential for ensuring proper fitment and safe driving. With a few basic tools, you can determine the correct thread diameter, pitch, seat type, and length, helping you avoid mistakes when replacing or upgrading wheels.

Step 1: Gather the Tools
Before starting, collect the necessary tools: a thread pitch gauge, caliper or ruler, and the existing lug nut. These tools will help you measure accurately. Having the right equipment ensures you can determine the lug nut size precisely, preventing damage to studs or mismatched purchases.
Step 2: Measure the Stud Diameter
Use a caliper or ruler to measure the diameter of the wheel stud. This is typically expressed in millimeters (M12, M14) or inches (1/2″, 7/16″). Correct measurement ensures that the lug nut threads will match the stud, allowing for secure installation and safe driving.
Step 3: Determine the Thread Pitch
Thread pitch is the distance between threads. Using a thread pitch gauge, check how far apart the threads are. Common examples include M12x1.25 or M12x1.5. Identifying the correct pitch prevents cross-threading and ensures the lug nut seats correctly for proper torque application.
Step 4: Identify the Seat Type
Examine the lug nut’s contact area with the wheel to determine the seat type—conical (acorn), ball (radius), flat, or mag. Matching the seat type to your wheel is crucial to avoid vibrations, uneven pressure, or wheel damage, especially with aftermarket or European-style wheels.
Step 5: Measure Lug Nut Length
Finally, measure the length of the lug nut from base to tip. This is especially important for aftermarket wheels, which may require longer nuts for proper thread engagement. Using the correct length ensures secure fastening, prevents stripped threads, and maintains safe wheel alignment.
Also Read:
Common Lug Nut Mistakes to Avoid
Even small errors when installing lug nuts can cause serious damage to wheels, studs, and brakes. Common mistakes include mismatched seat types, incorrect thread pitch, over-tightening, ignoring torque specs, or reusing damaged nuts. Avoiding these errors ensures safe driving, prevents costly repairs, and maintains proper wheel performance.
- Mixing ball seat and conical seat lug nuts
- Over-tightening with an impact gun
- Using incorrect thread pitch
- Ignoring torque specifications
- Reusing damaged or swollen lug nuts
These mistakes often lead to expensive repairs.
When Should You Replace Lug Nuts?
Lug nuts may seem durable, but wear and damage can compromise safety. Replace them if you notice rounded edges, rust, cracked seats, loose fitting, or after installing new wheels. Properly replacing worn lug nuts is an inexpensive step that prevents wheel damage and ensures safe, reliable driving.
Replace lug nuts if you notice:
- Rounded edges
- Rust or corrosion
- Cracked seats
- Loose fitting
- After wheel upgrades
Lug nuts are inexpensive compared to the damage they can cause.
Also Read:
Safety Tips for Lug Nut Installation
Correct installation of lug nuts is essential for wheel safety and longevity. Always hand-thread first, tighten in a star pattern, and use a torque wrench. Recheck torque after driving 50–100 miles and avoid lubricating threads unless specified. Following these steps prevents loose wheels, vibrations, and potential accidents.
- Always hand-thread first
- Tighten in a star pattern
- Use a torque wrench
- Recheck torque after 50–100 miles
- Avoid lubricating threads unless specified
Final Thoughts
Understanding wheel lug nut sizes is not just for mechanics—it’s essential knowledge for every vehicle owner. From selecting the right thread size and pitch to matching the correct seat type and torque, every detail matters.
By using the lug nut size charts in this guide and following proper installation practices, you can ensure safer driving, longer wheel life, and peace of mind on every journey.
If you’re ever unsure, always double-check your vehicle manual or consult a professional—but now, you’re equipped with the knowledge to make the right choice.
Also Read:

