Casting, in the realm of manufacturing, innovation is the heartbeat that propels industries forward. One such innovation that has significantly transformed the manufacturing landscape is casting. Casting is not merely a process, it’s an art form that melds science, technology, and creativity to shape raw materials into intricate and precise components. In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the world of casting, exploring its techniques, applications, and impact on various industries.
Understanding Casting: A Primer
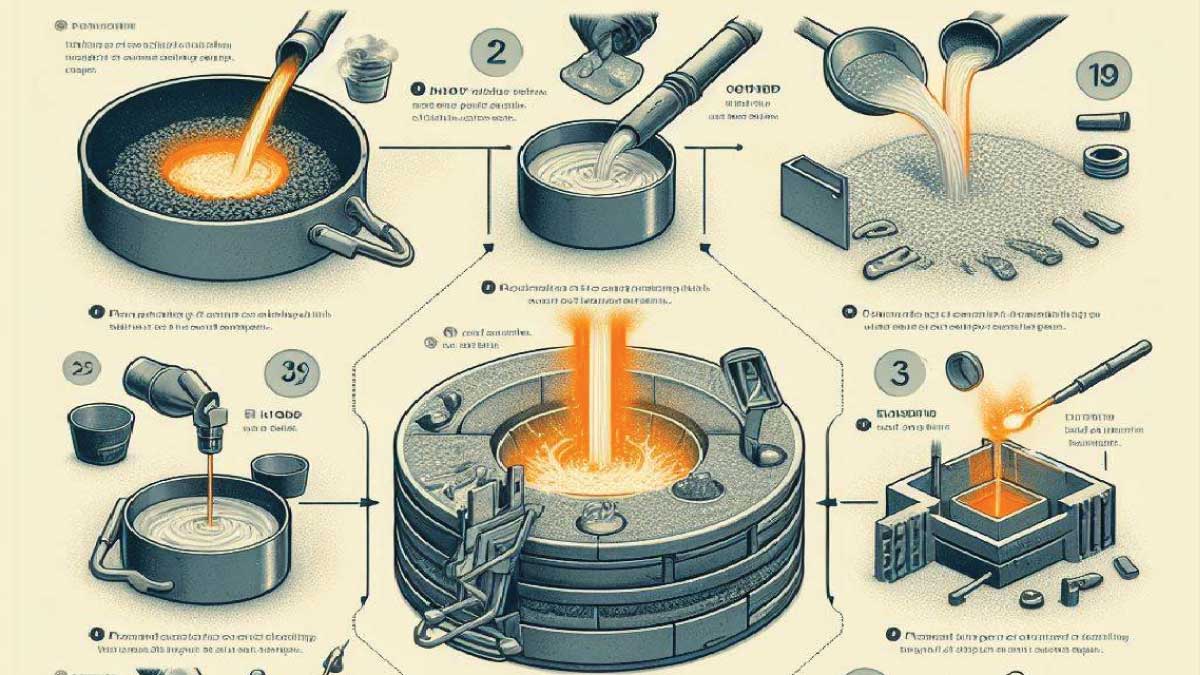
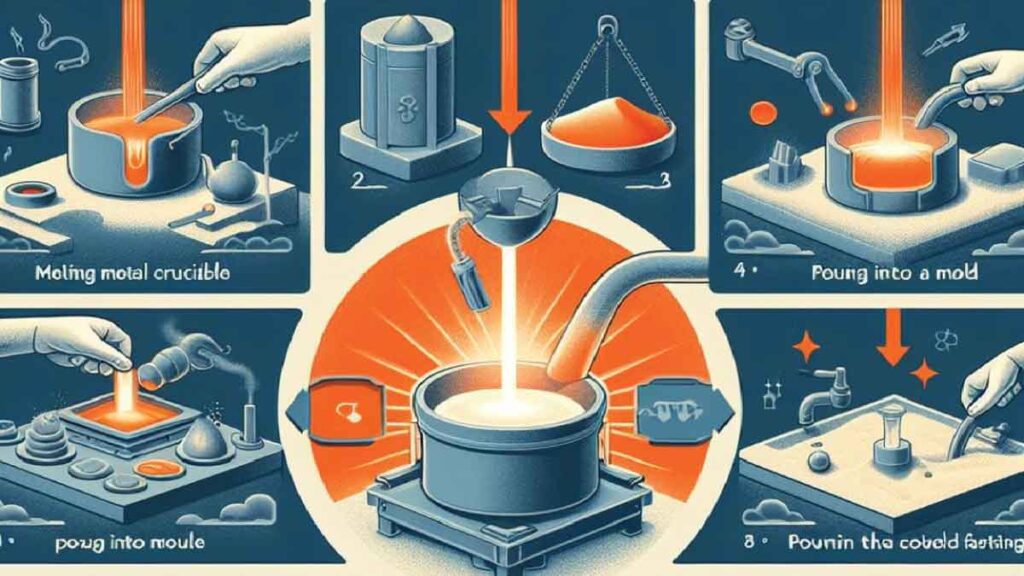
At its core, casting involves the pouring of a liquid material into a mold, which then solidifies to form the desired shape. This process dates back thousands of years, with early civilizations utilizing casting techniques to craft tools, weapons, and ornaments. However, modern casting methods have evolved exponentially, thanks to advancements in materials science and engineering.
Casting Techniques
The casting process is a multifaceted realm, encompassing various methods meticulously tailored to suit specific applications and materials. Manufacturers are presented with a plethora of options, each offering unique advantages and capabilities. Let’s delve into some of the most common casting techniques:
Sand Casting
Sand casting, revered as one of the oldest forms of casting, maintains its prominence due to its simplicity and adaptability. In this method, a pattern is intricately pressed into sand to form a mold cavity. Molten metal is then poured into this cavity, taking the shape of the pattern. Once cooled, the sand mold is meticulously broken away, unveiling the casted part. This time-honored technique finds widespread use in the production of various components, ranging from intricate art pieces to robust industrial parts.
Investment Casting
Also known as lost-wax casting, investment casting stands as a pinnacle of precision and craftsmanship in the casting realm. This intricate process begins with the creation of a wax pattern, meticulously sculpted to the desired shape. The wax pattern is then coated with a refractory material, forming a mold. Upon heating, the wax melts away, leaving behind a hollow mold cavity. Molten metal is poured into this cavity, allowing for the creation of intricate and detailed parts with remarkable accuracy. Investment casting finds extensive application in industries where precision and intricacy are paramount, such as aerospace, automotive, and jewelry manufacturing.
Die Casting
Die casting emerges as a beacon of efficiency and repeatability, particularly suited for high-volume production of complex parts. In this method, molten metal is forcibly injected into a steel mold cavity under high pressure. Once the metal solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected, ready for further processing. Die casting boasts rapid production cycles and tight tolerances, making it indispensable in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods manufacturing.
Casting Applications Across Industries
The versatility of casting transcends boundaries, permeating a multitude of industries with its wide-ranging applications. Let’s delve into some key sectors where casting serves as a cornerstone of manufacturing:
Automotive Industry
In the fast-paced realm of automotive manufacturing, casting plays an indispensable role in shaping critical components essential for vehicle performance and functionality. Engine blocks, transmission housings, and chassis parts are just a few examples of components that rely on casting processes for their production. Die casting, renowned for its ability to produce lightweight yet robust parts, is particularly favored in the automotive sector. By leveraging die casting techniques, manufacturers can achieve the delicate balance between strength and weight, crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and overall performance.
Aerospace and Defense
Precision is paramount in the aerospace and defense sectors, where the integrity of every component is critical to safety and reliability. Casting technologies find extensive use in fabricating intricate components such as turbine blades, aircraft fuselages, and missile casings. Investment casting, prized for its ability to produce complex geometries with exceptional accuracy, holds a special place in these industries. By harnessing the precision of investment casting, aerospace and defense manufacturers can ensure the seamless integration of components, contributing to the safety and efficiency of aerospace systems.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical device industry demands uncompromising precision and biocompatibility in component fabrication, making casting an indispensable manufacturing technique. From implants and prosthetics to surgical instruments, casting processes enable the creation of intricate medical components tailored to the unique needs of patients. Investment casting, with its ability to produce intricate and biocompatible parts, emerges as a preferred choice in medical device manufacturing. By leveraging investment casting, manufacturers can ensure the precise fit and functionality of medical components, contributing to the advancement of healthcare technologies and treatments.
Art and Sculpture
Beyond its industrial applications, casting serves as a medium of artistic expression, allowing artists to breathe life into their creative visions. From timeless bronze sculptures to contemporary installations, casting techniques enable artists to realize intricate designs and forms with remarkable fidelity. Whether it’s the precision of investment casting or the versatility of sand casting, artists harness the transformative power of casting to push the boundaries of artistic expression. By embracing casting as a medium, artists create captivating works that resonate with audiences, enriching the cultural landscape and inspiring generations to come.
FAQs Related to Casting Processes:
What is casting in manufacturing?
Casting in manufacturing refers to the process of shaping molten material, typically metal, into a desired form by pouring it into a mold. Once the material solidifies, the mold is removed, leaving behind the casted part.
What are the different types of casting methods?
There are several types of casting methods, including sand casting, investment casting, die casting, and continuous casting. Each method offers unique advantages and is suited to specific applications and materials.
What industries use casting processes?
Casting processes are utilized across a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, defense, medical device manufacturing, and art. These industries rely on casting for producing a variety of components, from engine parts to intricate sculptures.
How does 3D printing impact casting processes?
3D printing has revolutionized casting processes by enabling the direct production of intricate molds and patterns. This reduces lead times, allows for design optimization, and facilitates customization, thereby enhancing efficiency and opening up new possibilities in casting.
What are the advantages of investment casting?
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, offers several advantages, including the ability to produce intricate and detailed parts with high accuracy, excellent surface finish, and the capability to cast various metals and alloys. Additionally, investment casting minimizes material wastage and allows for complex geometries that may be challenging to achieve with other casting methods.

HA Chaudhary is an experienced engineer with 15 years in the mechanical and industrial sectors. Holding advanced degrees and multiple certifications in engineering, he combines technical expertise with a passion for writing to provide valuable insights into engineering innovations and business strategies. His content empowers professionals to excel in their fields and stay updated with the latest industry trends.