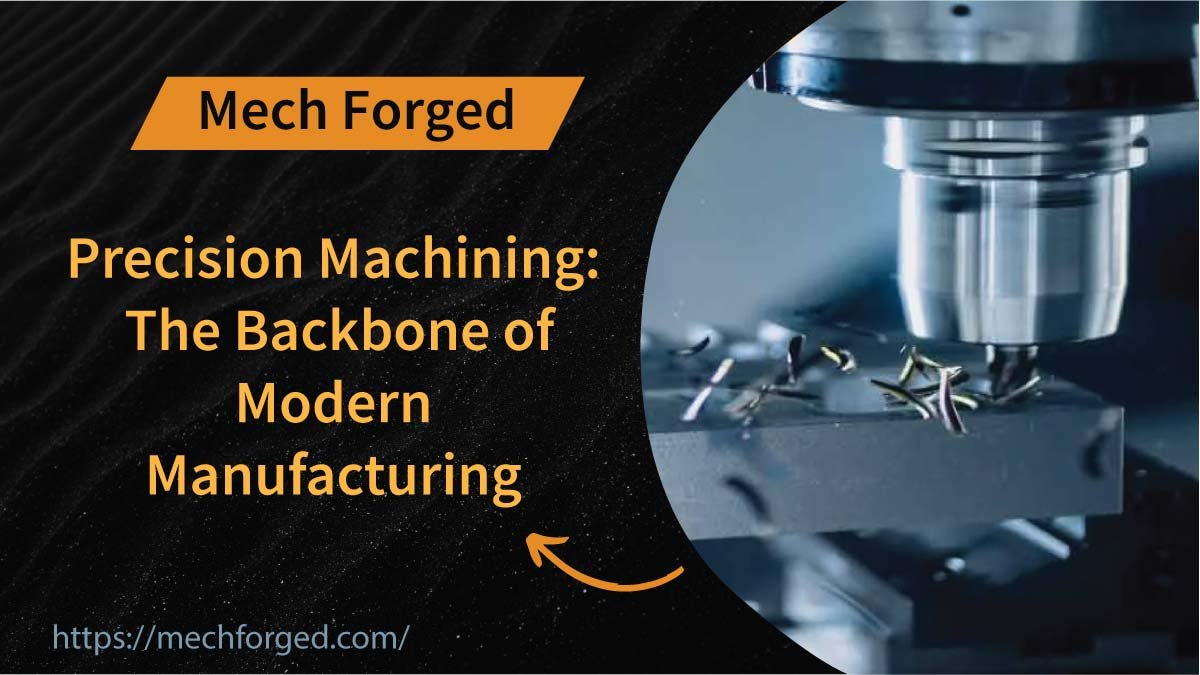
When I first stepped into a machine shop during a college field trip, the rhythmic hum of high-speed cutting tools, the scent of coolants, and the tight tolerance components being carved out of solid metal instantly caught my attention. It felt like stepping into the future, except this “future” had been around for decades, powering everything from aerospace innovations to medical breakthroughs. That was the day I truly appreciated the real meaning and impact of precision machining.
If you are even remotely connected to manufacturing, engineering, or product development in the USA, chances are precision machining plays a vital role in what you do or in what supports your lifestyle. Whether it’s the gear inside your car’s transmission, the aluminum housing of your laptop, or even surgical tools used in hospitals, precision machining is behind the scenes, quietly shaping our world.
What is Precision Machining?
At its core, precision machining is the process of removing material from a workpiece, typically metal or plastic to create parts with extremely tight tolerances. We’re talking about measurements down to a thousandth of an inch or even microns. It’s the art and science of turning blueprints into physical reality with pinpoint accuracy.
But it’s not just about cutting. Precision machining is about consistency, repeatability, and quality. Using CNC machines, lathes, milling machines, EDMs, and grinders, machinists sculpt raw materials into components that must fit and function perfectly especially in industries where failure is not an option.
My First Real Encounter with a CNC Mill
I remember working on a prototype project during my engineering internship. We had a small aluminum part designed in CAD, and it looked simple on screen. But when I handed it to the machinist, he just chuckled and said, “This’ll be fun.” I didn’t get it at first, but over the next three days, I watched as he set up the CNC mill, dialed in the tooling, tested feeds and speeds, and finally cut that block of aluminum into the exact shape we’d imagined—down to a 0.001” tolerance.
Seeing that level of precision unfold in real time completely shifted how I viewed manufacturing. I began to understand that precision machining isn’t just another industrial process—it’s a craft, a blend of engineering knowledge and real hands-on skill.
Why Precision Machining Matters More Than Ever
In today’s world, there’s zero room for error. Whether you’re building components for an aircraft turbine, a robotic arm, or a medical implant, the demand for accuracy and quality control is non-negotiable.
In the USA, where many industries are held to high regulatory standards—like the FDA for medical devices or the FAA for aerospace—precision machining is not optional; it’s essential.
Moreover, we’re seeing a massive resurgence of interest in American-made, high-quality components, especially with supply chain uncertainties post-pandemic. Companies are now leaning on domestic shops that specialize in precision CNC machining, tight tolerance parts, and custom prototyping. It’s a huge opportunity for both machinists and manufacturers.
Types of Precision Machining Processes
Let’s break down some of the main methods you’ll find in a precision shop:
1. CNC Milling:
CNC mills use rotating cutting tools to remove material. Think of them as very smart drills that can move in multiple axes. They’re ideal for producing complex geometries, slots, holes, and contours. If you’ve ever held a smartphone case or aerospace bracket, chances are it was milled to spec using a CNC machine.
2. CNC Turning:
Lathes rotate the workpiece itself while cutting tools shape it. This process is perfect for cylindrical parts—like shafts, bushings, and threads. Precision turning can achieve mirror finishes and micrometer-level tolerances.
3. Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM):
This process uses electrical sparks to erode material, particularly useful for hard metals or intricate internal geometries. It’s a go-to method for die-making and aerospace components.
4. Grinding and Finishing:
Grinding is where the final touch happens, refining surfaces and achieving the ultra-precise dimensions needed for critical parts. In many cases, it’s what takes a “rough” CNC-milled part and turns it into a customer-ready component.
5. Drilling, Boring, and Tapping:
These traditional operations are still part of most precision workflows. They may seem basic, but when you are drilling a hole to fit a bearing with a 0.001″ clearance, there’s no margin for error.
Precision Machining Materials: It’s Not Just Metal
Most people associate machining with steel or aluminum, but modern precision shops handle a wide range of materials. Some of the most common include:
Stainless Steel (used in medical, aerospace, and food processing)
Aluminum (lightweight and easy to machine)
Titanium (used in aerospace and medical implants)
Plastics like Delrin, PEEK, and PTFE (used in medical and electrical applications)
Brass and Copper (used in electrical and plumbing components)
Every material has its quirks—how it reacts to heat, how it holds tolerance, how fast it can be cut. A good machinist knows how to work with the strengths and weaknesses of each.
Quality Control: Where Precision Becomes Reality
You can’t talk about precision machining without talking about quality control. Every part that leaves a high-end shop is measured, inspected, and often tested. From CMM machines (coordinate measuring machines) to laser scanners, the tools used to verify precision are just as advanced as the machines that produce the parts.
I once visited a medical machining facility in Ohio, and they showed me their inspection lab. It looked more like a science lab than a factory—climate-controlled rooms, white gloves, and machines that could detect surface deviations invisible to the human eye. That level of dedication is what makes precision machining so vital to mission-critical industries.
The Rise of CNC Prototyping and Short-Run Production
With startups and R&D teams needing quick iterations, CNC prototyping has exploded in popularity. Instead of waiting weeks for injection molding tools, engineers can now machine a functional prototype in days or even hours. That speed can make or break innovation cycles.
I have personally worked with a few teams who used rapid CNC machining to refine their products before investing in mass production. It saved them tens of thousands of dollars by catching design flaws early. The flexibility of short-run CNC production also allows for custom solutions tailored to each client’s needs.
Careers in Precision Machining: More Than Just Blue-Collar Work
One thing that always surprises outsiders is how much thought, creativity, and knowledge goes into being a machinist. It’s not about just pushing buttons. You need to understand metallurgy, geometry, software (like CAD/CAM), and machine dynamics.
Skilled CNC machinists and programmers are in high demand across the USA. With the growth of automation and advanced manufacturing, precision machining is becoming more technical and more rewarding. You can build a solid career without a traditional four-year degree and still earn a great living.
Plus, there’s real satisfaction in holding a finished part you created. Whether it ends up in a fighter jet or a spinal implant, you know your work made a difference.
Sustainability and Efficiency: The Future of Precision Machining
As manufacturing evolves, so does the emphasis on sustainability. Precision machining shops are adopting practices like:
Recycling metal chips
Using eco-friendly coolants
Optimizing material usage to reduce waste
Investing in energy-efficient machines
Additionally, with digital twins, simulation software, and smart manufacturing tools, companies can now model entire machining processes before a single cut is made. That means fewer mistakes, better part yields, and more cost-effective runs.
Final Thoughts: Why Precision Machining Deserves Your Attention
Whether you are an engineer, entrepreneur, student, or just someone curious about how things are made, precision machining is worth learning about. It’s where design meets physical reality, and where skill meets science. In the USA, we have some of the most advanced machining capabilities in the world and a legacy of innovation that continues to grow.
If you have ever held a perfectly machined part in your hand, you know there’s something special about it. It’s solid, smooth, exact. That’s the power of precision.
And if you’re in a business that depends on reliability, consistency, or innovation, whether you are designing drones, medical devices, custom hardware, or electric vehicles, precision machining might just be the partner your ideas need.
Let me know in the comments if you have worked with a precision shop or have any stories to share. Or if you are thinking about diving into this field, I’d love to hear what interests you most. Sharing knowledge is how we all move forward, accurately, efficiently, and yes, precisely.
Also Read:
FAQs About Precision Machining
What is precision machining used for?
Precision machining is used to create highly accurate and consistent parts for industries like aerospace, medical, automotive, electronics, and robotics. It’s essential for producing components with tight tolerances, ensuring they fit and function exactly as designed.
What materials are commonly used in precision machining?
Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, brass, copper, and high-performance plastics like PEEK and Delrin. The choice of material depends on the part’s function, durability, and industry requirements.
How accurate is precision machining?
Precision machining can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.0001 inches, depending on the machine, tools, and material used. This level of accuracy is critical for applications where even minor deviations could cause failure.
Is CNC machining the same as precision machining?
Not exactly. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a method often used in precision machining. While all CNC machining can be precise, precision machining specifically focuses on achieving extremely tight tolerances and high repeatability, often with additional quality control measures.
How long does it take to produce a precision machined part?
It varies based on complexity, material, and shop workload. Simple parts may take a few hours, while complex components might require several days, especially when tight tolerances and post-processing are involved.
Why is precision machining important in the medical industry?
Because patient safety depends on it. Precision machining is used to manufacture surgical instruments, implants, diagnostic devices, and more, where dimensional accuracy, biocompatibility, and sterility are critical.
Is precision machining expensive?
It can be more costly than standard machining due to the equipment, expertise, and time involved. However, the higher quality and performance of the parts often justify the investment—especially in mission-critical applications.
Can small businesses benefit from precision machining?
Absolutely. Many precision machine shops work with startups and small businesses for prototyping, short-run production, or custom parts. With the rise of digital manufacturing, it’s easier than ever to access precision services without large-scale production.
What software is used in precision machining?
Common CAD/CAM software includes SolidWorks, Fusion 360, Mastercam, AutoCAD, and Siemens NX. These tools help design parts, simulate machining processes, and program CNC machines accurately.
Is there a future in precision machining careers?
Definitely. With automation, reshoring, and advanced manufacturing on the rise in the U.S., skilled CNC machinists, programmers, and manufacturing engineers are in high demand. It’s a rewarding, hands-on career with strong growth potential.