“Types of File Tools” are essential instruments across diverse industries and hobbies, entrusted with the precise shaping and smoothing of materials. Whether in woodworking, metalworking, or other crafts, “Types of File Tools” exhibit a diverse array of shapes, sizes, and materials, each meticulously crafted to suit particular tasks and materials. In our exploration of 10 distinct file types, we uncover their varied compositions and applications, shedding light on their indispensable roles in facilitating precision workmanship. From the robust steel construction of flat files to the precision-engineered diamond surfaces of specialty files, each variant brings its own unique capabilities to the crafting table.
As we delve deeper into their uses and materials, we gain a deeper appreciation for the nuanced craftsmanship and ingenuity that underpin these essential tools, empowering artisans and craftsmen to bring their creative visions to life with meticulous precision and finesse.
Table of Contents
Toggle10 Different Types of File Tools
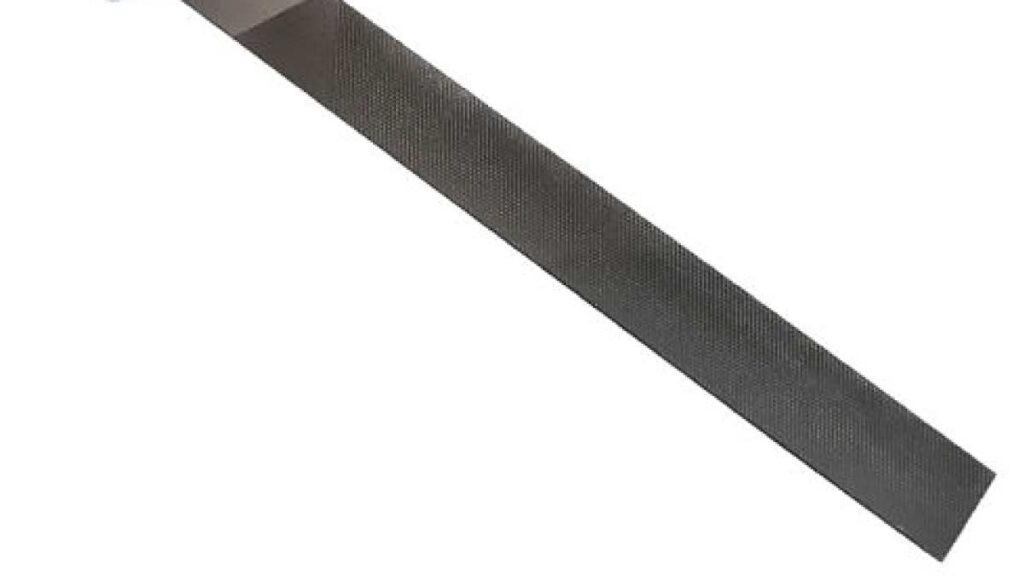

1. Flat File:
Flat files, typically crafted from hardened steel, stand as the workhorse among file tools. Their versatility spans across various materials such as wood, metal, and plastic. Available in a spectrum of lengths and widths, they cater to a plethora of applications. Whether it’s leveling a rough metal surface or smoothing out imperfections in a wooden plank, the flat file’s reliability remains unmatched.
The hardened steel composition of flat files ensures durability and longevity, even when subjected to rigorous filing tasks. Their flat surface provides ample contact area, allowing for efficient material removal while maintaining straight edges and surfaces. Woodworkers rely on flat files to refine joints, shape edges, and remove excess material, ensuring precise fits in their projects. Similarly, metalworkers utilize flat files to smooth welds, deburr sharp edges, and shape metal components with precision.
In plastic fabrication, flat files are indispensable for smoothing rough edges, refining contours, and achieving seamless finishes. Whether it’s trimming plastic pipes or shaping custom plastic parts, these files offer the versatility and control necessary for achieving professional results. Available in various lengths and widths, flat files accommodate different project requirements, from intricate detailing to broader surface leveling.
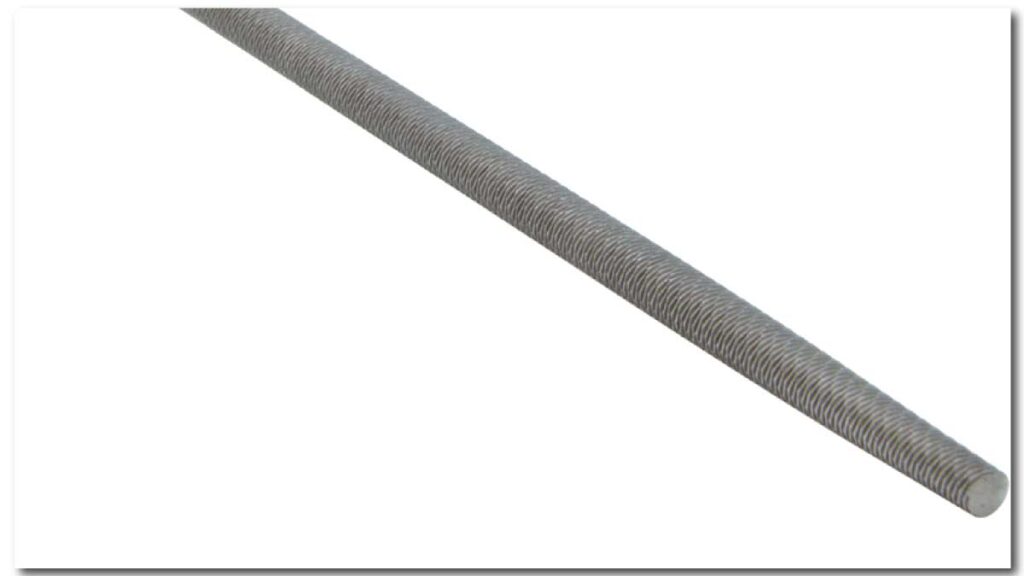

2. Round File:
Forged from hardened steel or high-speed steel, round files present a distinctive rounded cross-section. Their specialized design makes them indispensable for tasks like enlarging round holes, shaping concave surfaces, and refining curved edges. Commonly found in the arsenals of metalworkers and locksmiths, these files offer precision and efficiency in shaping metal components.
Round files excel in tasks that require the removal of material from curved surfaces while maintaining smooth contours. Metalworkers utilize them to enlarge bolt holes, shape keyways, and refine gear teeth, ensuring precise fits and smooth operation of mechanical components. Locksmiths rely on round files for shaping keyways and adjusting lock components to achieve optimal functionality.
In automotive repair and maintenance, round files find application in tasks such as shaping metal body panels, enlarging holes for bolts or rivets, and refining intricate contours for seamless repairs. Their robust construction and ergonomic design make them ideal for prolonged use in demanding environments, ensuring consistent performance and longevity.
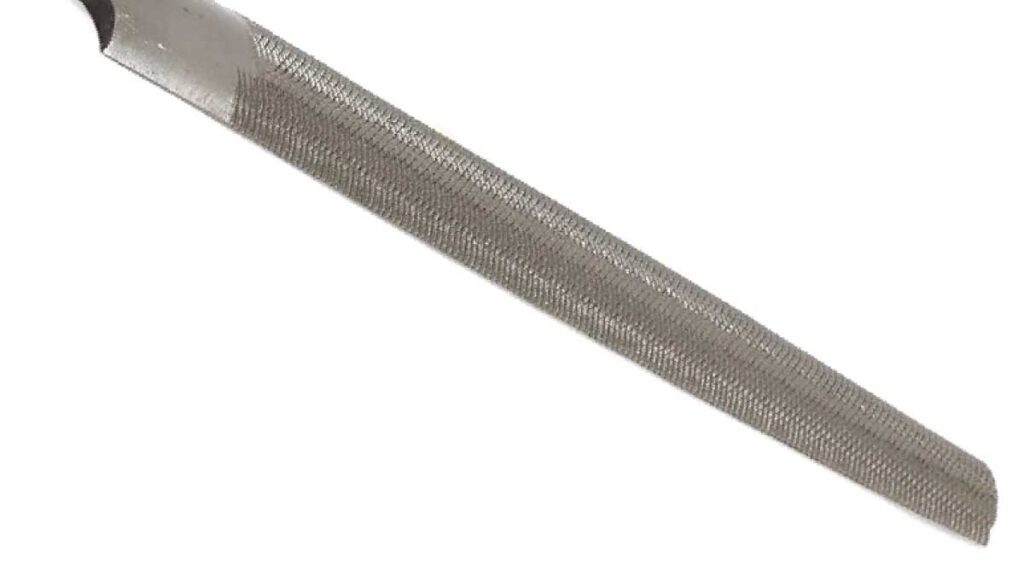

3. Half-Round File:
Combining the features of flat and round files, half-round files boast one flat and one rounded side. This unique configuration renders them suitable for addressing both flat and curved surfaces with ease. From metalworking to woodworking, these files find utility in a myriad of applications, whether it’s smoothing out a metal weld or refining the contours of a wooden sculpture.
Metalworkers rely on half-round files for blending curved and flat surfaces, smoothing weld seams, and shaping intricate metal components. The flat side allows for precise material removal on flat surfaces, while the rounded side facilitates shaping concave curves and rounded edges with accuracy. Woodworkers utilize half-round files for shaping curved elements, refining concave surfaces, and sculpting intricate details in wooden projects.
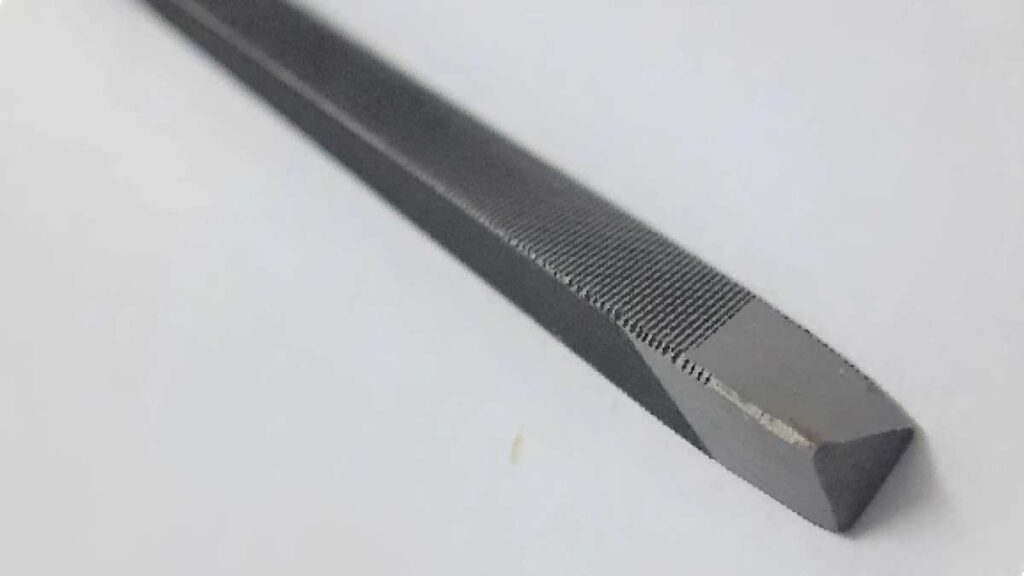

4. Triangle File:
Crafted from hardened steel, triangle files feature three flat sides, facilitating precise filing of acute angles and corners. Machinists and metalworkers often rely on these specialized files for intricate tasks that demand meticulous attention to detail. From shaping intricate metalwork to refining delicate mechanical parts, triangle files excel in precision filing tasks.
Triangle files are indispensable for filing internal corners, creating precise angles, and shaping intricate details in metal and plastic components. Machinists utilize them for deburring internal corners in machined parts, ensuring smooth surfaces and precise fits. Model makers rely on triangle files for shaping miniature components, refining intricate details, and achieving precise contours in their creations.
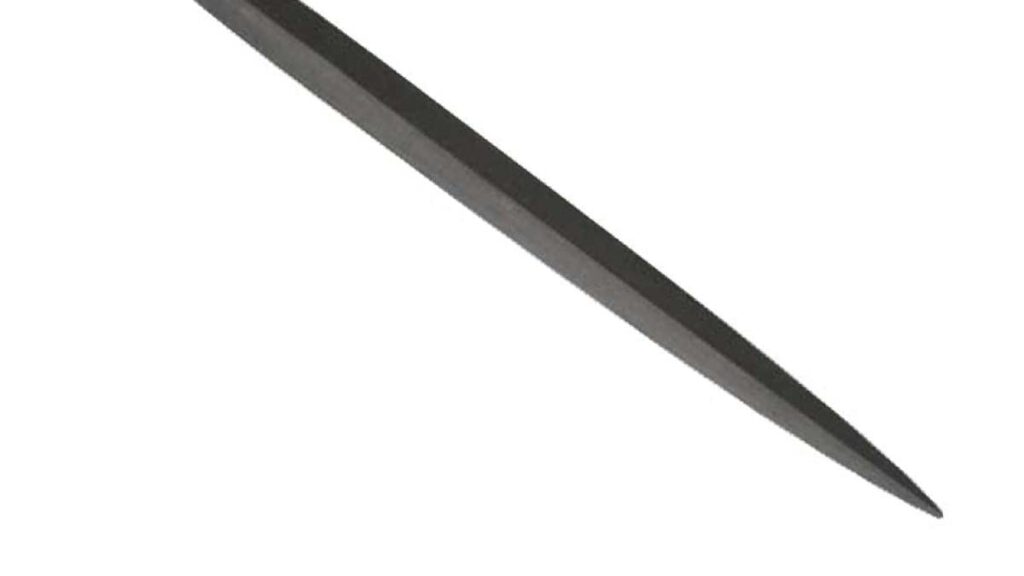

5. Needle File:
Precision reigns supreme with needle files, meticulously crafted from hardened steel or high-speed steel. Available in various cross-sectional shapes like flat, round, square, and triangular, they cater to the intricate demands of jewelry making, watchmaking, and model making. From shaping tiny gears to refining delicate jewelry pieces, needle files offer unparalleled precision and control.
Needle files are indispensable tools in tasks that require intricate detailing and precise shaping of small components. Jewelry makers rely on needle files for shaping and refining precious metals, setting gemstones, and creating intricate designs with precision. Watchmakers utilize needle files for shaping tiny gears, adjusting movement components, and ensuring precise fits in delicate timepieces. Model makers rely on needle files for shaping miniature parts, refining intricate details, and achieving precise contours in scale models and miniatures.
Related Posts:
30 Types of Wrenches and Their Uses
25 Types of Screwdrivers and Their Material and Uses
Mastering Pliers Maintenance: 7 Easy Steps with Tips
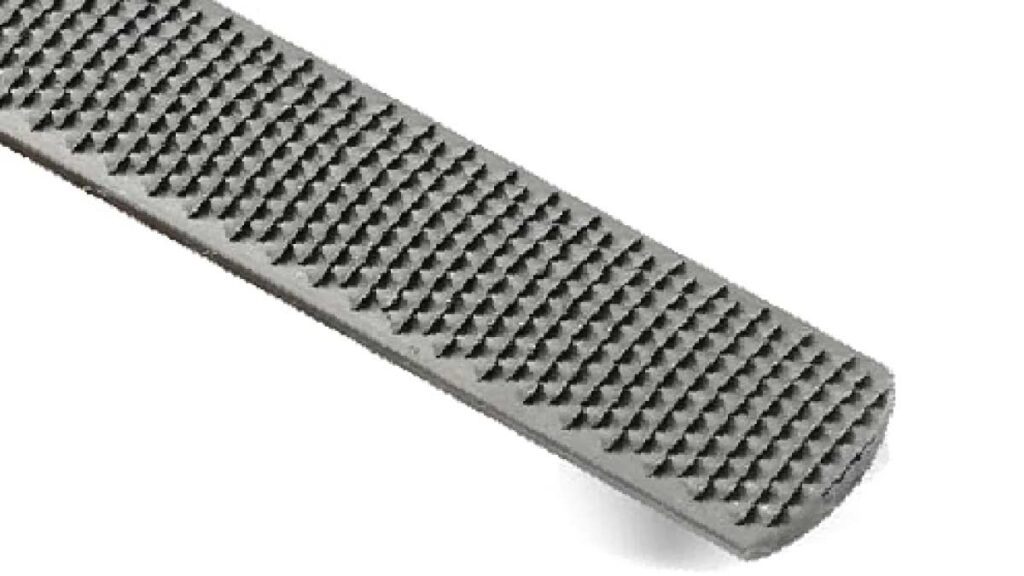

6. Rasp File:
Rasp files, typically made of high-carbon steel, are a staple in woodworking workshops for their unique coarse surface with individually cut teeth. This design makes them ideal for quickly removing material from wood, plastic, or soft metals. Whether it’s shaping rough contours or performing rough finishing work, rasp files are valued for their efficiency and versatility.
The high-carbon steel construction of rasp files ensures durability and longevity, even when subjected to heavy use. Their coarse teeth aggressively bite into the material, allowing woodworkers to quickly shape and smooth surfaces, remove material from intricate details, and achieve desired contours with ease. From shaping furniture components to rough carving sculptures, rasp files are indispensable tools in woodworking projects of all scales.
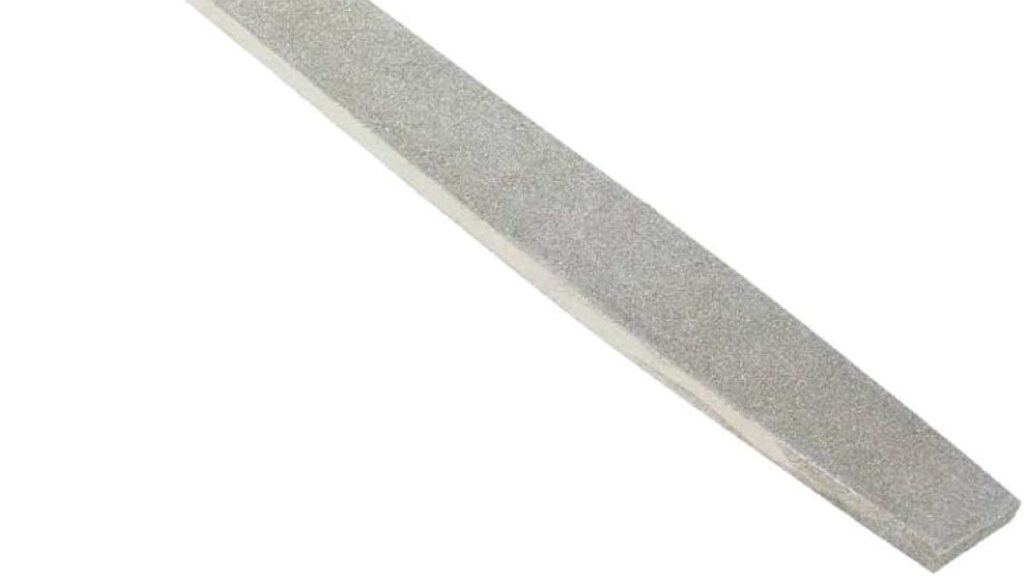

7. Diamond File:
Embedded diamond particles on a steel or aluminum base characterize diamond files, offering an abrasive surface made of industrial-grade diamonds. This composition provides exceptional hardness and durability, making diamond files the go-to choice for filing hard materials such as ceramics, glass, and hardened steel.
The abrasive surface of diamond files ensures precise material removal while maintaining smooth surfaces and edges. Glassworkers rely on diamond files for shaping and smoothing glass edges, creating intricate designs, and achieving precise angles in stained glass projects. Ceramic artists utilize diamond files for refining intricate details, smoothing rough surfaces, and achieving precise contours in ceramic sculptures and pottery. In metalworking, diamond files excel in shaping hardened steel components, deburring edges, and achieving precise fits in precision machining applications.

8. Cabinet File:
Crafted from hardened steel, cabinet files, also known as wood rasps, feature a curved surface with individually cut teeth. This specialized design makes them ideal for shaping and smoothing concave surfaces in woodworking projects, such as shaping chair seats or hollowing out bowls.
Woodworkers rely on cabinet files for shaping curved elements, refining concave surfaces, and achieving smooth transitions between contours. The curved surface of cabinet files allows for efficient material removal while maintaining control and precision. Whether it’s shaping intricate details in furniture components or smoothing out curves in decorative woodworking projects, cabinet files offer the versatility and control necessary for achieving professional results.

9. Chainsaw File:
Hardened steel construction characterizes chainsaw files, specifically designed for sharpening the teeth of chainsaw blades. With a round cross-section and available in various diameters to match different chain sizes and tooth configurations, chainsaw files ensure optimal performance and longevity of chainsaw blades.
Chainsaw operators rely on these specialized files for maintaining the sharpness and efficiency of chainsaw blades, ensuring clean cuts and minimal effort during cutting tasks. The round cross-section of chainsaw files allows for precise sharpening of individual teeth, ensuring uniformity and consistency in cutting performance across the entire chain. Whether it’s routine maintenance or restoring heavily worn blades, chainsaw files offer the precision and reliability necessary for maintaining peak cutting performance.

10. Machinist’s File:
Precision is paramount in machining operations, and machinist’s files, crafted from high-carbon steel or high-speed steel, rise to the challenge. With a smooth, parallel cutting surface, these precision tools are essential for fine finishing and fitting of metal parts, ensuring precise tolerances and smooth surfaces in machining applications.
Machinists rely on these specialized files for deburring edges, removing machining marks, and achieving precise fits in precision engineering projects. The smooth cutting surface of machinist’s files allows for precise material removal while minimizing surface imperfections, ensuring optimal functionality and performance of machined parts. Whether it’s finishing intricate components or refining critical surfaces in precision machinery, machinist’s files are indispensable tools for achieving the highest standards of quality and precision in machining operations.
Related Posts:
40 Different Types of Pliers and Their Uses
How to Read a Tape Measure? Easy Explanation
Torque Wrench: Read This Before You Buy
Conclusion About Types Of File Tools:
In summary, files stand as indispensable companions in diverse industries and hobbies, delivering meticulous shaping and smoothing prowess across an array of materials. Familiarizing oneself with the diverse types of files, their compositions, and applications proves crucial in selecting the perfect tool for each task and attaining impeccable outcomes. Whether you are sculpting wood, fashioning metal, crafting jewelry, or indulging in hobbies, the right file is akin to a trusted ally, elevating your projects with precision and finesse. So, whether you are refining intricate details or shaping substantial surfaces, the right file in your arsenal can truly be the linchpin in achieving your desired results with utmost efficiency and accuracy.
FAQs about File Tools Types:
What are the main types of file materials?
The main materials used in file tools are hardened steel, high-speed steel, high-carbon steel, and diamond particles embedded on a steel or aluminum base.
Can files be used on different materials?
Yes, files are versatile tools that can be used on various materials such as wood, metal, plastic, ceramics, glass, and hardened steel, depending on the type of file and its composition.
How do I choose the right file for my project?
Consider the material you’re working with, the desired outcome, and the specific tasks involved. Different types of files are designed for different purposes, so match the file type and material to achieve the best results.
Are file tools suitable for beginners?
Yes, file tools can be used by beginners with proper guidance and instruction. Start with basic file types and gradually expand your skills as you become more familiar with different materials and techniques.
How do I maintain and clean file tools?
To maintain file tools, regularly remove debris and buildup from the file teeth using a file card or wire brush. Store files in a clean, dry place to prevent rusting. Lubricate occasionally with a light oil to prevent corrosion and ensure smooth operation.
Can file tools be sharpened or reconditioned?
Yes, some file types can be sharpened or reconditioned using a file jointer or file card. However, it’s essential to follow proper sharpening techniques to maintain the file’s effectiveness and prolong its lifespan.
Are there safety precautions to consider when using file tools?
Yes, when using file tools, wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as gloves and safety glasses to protect against flying debris. Secure the workpiece firmly in place to prevent slipping or movement during filing. Additionally, be mindful of the direction of file strokes to avoid injury.

